AVL Tree program in Java
Just like the Red-Black Tree, the AVL tree is another self-balancing BST(Binary Search Tree) in Java. In the AVL tree, the difference between heights of the right and left subtree doesn't exceed one for all nodes. It takes O(h) time to perform the search, max, min, insert, and delete BST operations. Here, the h is the height of the Binary Search Tree.
Let's take an example of an AVL tree and a tree that is not AVL to understand the difference between both of them,
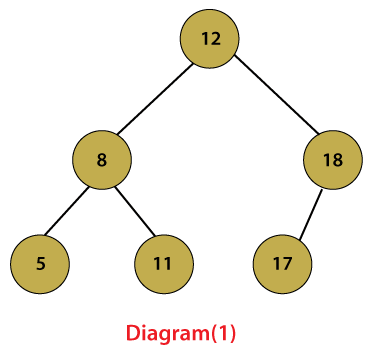 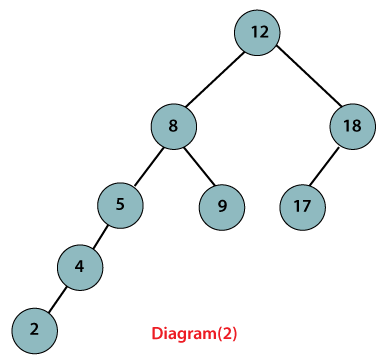
Diagram(1) is an example of the AVL tree because the difference between the heights of the left and right sub-tree is 1. Diagram (2) is not an AVL tree because the difference between the heights of the left and right subtree is not 1.
Algorithm
Let's understand the algorithm of inserting a node in the AVL Tree:
Suppose the newNode is the newly inserted node in the AVL Tree.
- We will insert the newNode in the AVL Tree by performing the standard BST insert operation.
- We will go through the AVL Tree from the newNode and check for that node that is unbalanced. Suppose unBalNode is the first unbalanced node, childNode is the child node of the unBalNode that comes on the path from newNode to unBalNode, and newNode is the grandchild of the unBalNode that comes from the path from newNode to unBalNode.
- After that, we perform the appropriate rotations on the subtree rooted with unBalNode to re-balance the AVL Tree. These are the following four cases which we need to be handled.
- When childNode is the left child of the unBalNode and newNode is the left child of the childNode. This case is known as Left Left Case.
- When the childNode is the left child of the unBalNode, and the newNode is the right child of the childNode. This case is known as Left Right Case.
- When the childNode is the right child of the unBalNode, and the newNode is the right child of the childNode. This case is known as Right Right Case.
- When the childNode is the right child of the unBalNode, and the newNode is the left child of the childNode. This case is known as Right Left Case.
- In all the cases which we have discussed above, the subtree rooted with the unBalNode is only needed to be re-balanced. After that, the complete tree will be balanced and the same as it was before insertion.
AVLTreeExample.java
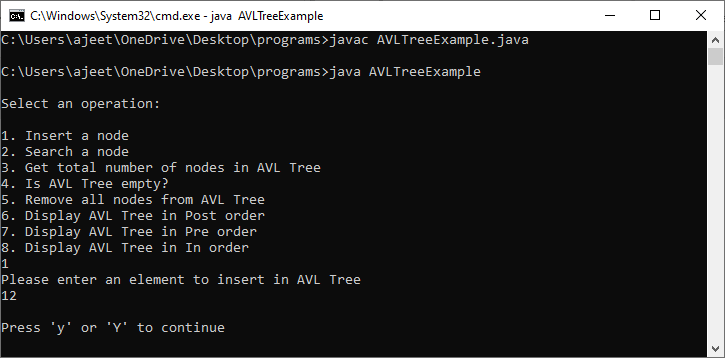
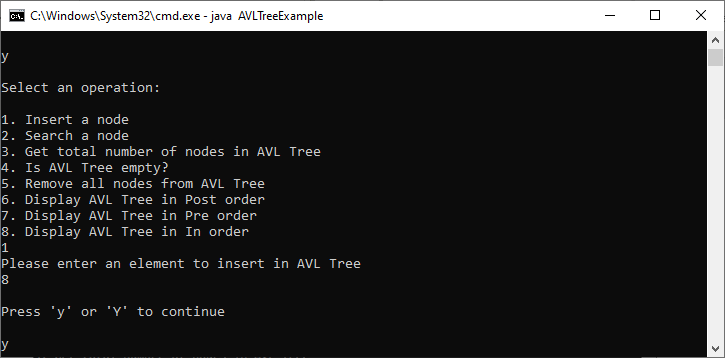
Output
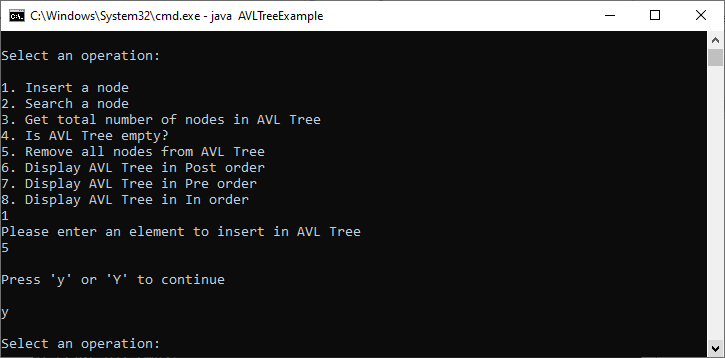
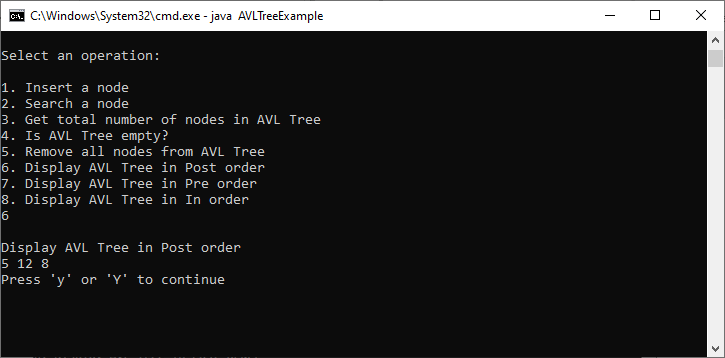
|






 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










