Difference between Basic Disk and Dynamic DiskBoth basic disk and dynamic disk are disk configurations available in Windows Operating System. A basic disk is the same as the configuration used with MS-DOS and Windows NT, and it has existed ever since the days of DOS, and Windows XP/2000 used basic disk configuration by default. However, Windows started using the concept of dynamic disks since Windows 2000. Both the disk configurations have different features, and they have their own advantages and disadvantages, but they are related somehow. Both disks configurations support FAT, FAT32, and NTFS file systems, except you cannot create a FAT32 dynamic volume. 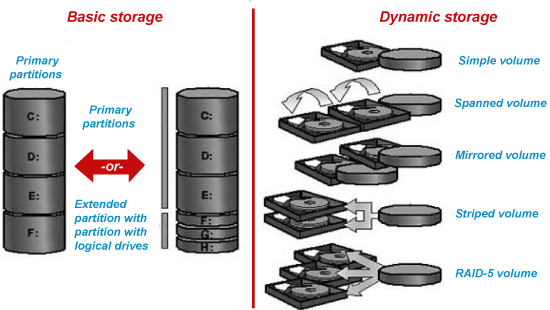 What is a Basic Disk?A basic disk is a type of hard drive configuration available with the Windows operating system. Normal partition tables or logical drives are used to manage all partitions and data on the hard disk, and they are the storage types most often used with Windows. It can contain four or three primary partitions and an extended partition with multiple logical drives. The following operations can be performed in basic disk configuration.
Basic disks provide a simple storage solution that can accommodate a useful array of changing storage requirement scenarios. Basic disks also support clustered disks, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 1394 disks, and universal serial bus (USB) removable drives. For backward compatibility, basic disks usually use the same Master Boot Record (MBR) partition style as the disks used by the Microsoft MS-DOS operating system and all versions of Windows. Still, they can also support GUID Partition Table (GPT) partitions on systems that support it. What is Dynamic Disk?A disk that has been initialized for dynamic storage is called a dynamic disk. It uses dynamic volumes to manage data. All volumes on dynamic disks are known as dynamic volumes, and dynamic Disk Configuration works on the concept of volumes. Dynamic disks provide features that basic disks do not, such as the ability to create volumes that span multiple disks (spanned and striped volumes) and the ability to create fault-tolerant volumes (mirrored and RAID-5 volumes). Dynamic disks offer greater flexibility for volume management because they use a database to track information about dynamic volumes on the disk and other dynamic disks in the computer. Because each dynamic disk in the computer stores a replica of the dynamic disk database. For example, a corrupted dynamic disk can repair one by using the database on another dynamic disk. The partition style of the disk determines the location of the database. On MBR partitions, the database is contained in the last 1 megabyte (MB) of the disk. On GPT partitions, the database is contained in a 1-MB reserved (hidden) partition. Dynamic disks are a separate form of volume management that allows volumes to have non-contiguous extents on one or more physical disks. Dynamic disks and volumes rely on the Logical Disk Manager (LDM), Virtual Disk Service (VDS), and their associated features. These features enable you to convert basic disks into dynamic disks and create fault-tolerant volumes. Multi-partition volume support was removed from basic disks and is now exclusively supported on dynamic disks to encourage dynamic disks. The following operations can be performed only on dynamic disks:
Difference between Basic Disk and Dynamic DiskMost hard disks use two types of configuration to store the information in them. These configurations are basic disk and dynamic disks. Although both of these configurations store data efficiently, but they work on different principles and offer different features.  The difference between Basic Disk and Dynamic Disk is that the basic disk is a traditional Window-based hard disk data storage configuration that uses MBR and GPT partition where partition extension is impossible. In contrast, a dynamic disk is the latest data configuration format that uses LDM and VDS features where partition extension is possible. Another difference between basic and dynamic disks is that dynamic disk volumes can be composed of non-contiguous extents on one or multiple physical disks. By contrast, a volume on a basic disk consists of one set of contiguous extents on a single disk. Because of the location and size of the disk space needed by the LDM database, Windows cannot convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk unless there is at least 1 MB of unused space on the disk. Below are some more important differences between Basic Disk and Dynamic Disk, such as:
Next TopicWhat is Zombie Process |