Blood Sugar LevelThe amount of glucose, or sugar, in a person's blood at any particular time is known as the blood glucose level. Medical care will be required if a person experiences a high or a low blood sugar level in their body. It is because high or low blood sugar levels negatively affect the body's functioning and can sometimes become very lethal.  Average Blood Sugar LevelsThe blood sugar level is determined by the amount of sugar or glucose in the human body. If the amount of glucose is higher than the normal amount, it is said to be a high blood sugar level. Similarly, if the amount of glucose is less than the normal blood glucose level, then it is said to be a low blood sugar level. A basic sugar called glucose is constantly present in the bloodstream. Blood glucose levels can be checked at any time, including when someone is fasting (first thing in the morning), before, or right after eating. Adults without diabetes should have fewer than 100 mg/dL of blood glucose when fasting for at least eight hours. Adults without diabetes should have blood glucose levels between 90 and 110 mg/dL two hours after eating. Blood sugar levels fluctuate during the day due to a variety of factors:
Regardless of age, anyone without diabetes or prediabetes should have a morning blood sugar level of less than 100 mg/dL. 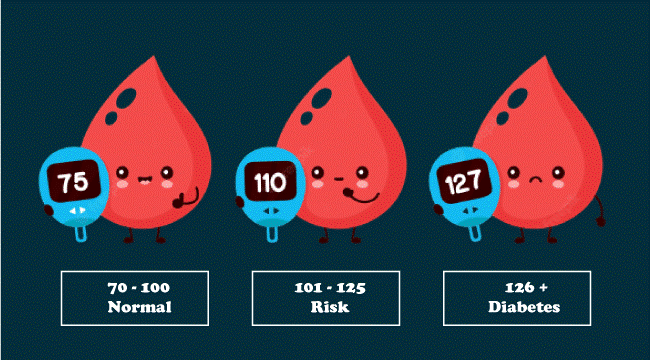 Types of DiabetesHere is a quick introduction to the many types of diabetes before discussing blood sugar levels. Type 1 DiabetesType 1 diabetes is developed when the body's immune system destroys the pancreatic cells. Diet or way of life has little impact on type 1 diabetes. Pancreatic cells secrete insulin, and when the pancreatic cells are destroyed, no more insulin is being secreted in the body, and blood suffers from insulin deficiency. Therefore, this type of diabetes is also called insulin-dependent diabetes. It is observed that, although type 1 diabetes is age-independent and can happen to a person of any age group, kids and young adults frequently suffer from type 1 diabetes. Since it happens due to a failure of pancreatic cells, which cannot be regenerated again, it is a disease with no treatment known yet. Once a person has developed type 1 diabetes, there is no way to cure it or prevent it any further.  To balance the effect of the amount of insulin in the body, people suffering from type 1 diabetes inject insulin from outside the body. While maintaining a nutritious diet and exercising regularly is beneficial for everyone, people with type 1 diabetes will always require insulin (regardless of what they eat) to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Various types of insulin are used by people suffering from type 1 diabetes. For instance, basal insulin, administered by pump or injection once or twice daily, maintains blood sugar levels during fasting. Additionally, fast-acting insulin is utilized to support the body's digestion of food and to lower blood sugar levels as needed. Type 2 DiabetesJust like type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes is also not limited to people of a particular age group. But it has been observed that it is more common in people with agar 45 or above. In type 2 diabetes, cells do not react to insulin as they should. Insulin resistance is what causes this. In order to produce more insulin, the pancreas must work harder; eventually, it is unable to do so, and blood sugar levels rise. There are so many factors which can become the cause of type 2 diabetes. Some of them are:
Diet, exercise, and oral medications are used to regulate blood sugar in persons with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, injectable drugs (such as insulin or other drugs that are not insulin but assist lower blood sugar) are occasionally utilized.  Pregnancy DiabetesPregnant women can sometimes develop gestational diabetes. If a soon-to-be-a-mother is suffering from gestational diabetes, there is a high chance that the baby will also get the disease from its mother. But in most cases, the health concerning issues of gestational diabetes are nullified upon delivery. However, your likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes in later life will be higher. Additionally, your child is more likely to be obese during childhood and adolescence and to acquire type 2 diabetes in the future. Women with gestational diabetes will be advised to alter their diets, increase their physical activity, and be regularly watched. To assist in lower blood sugar levels, insulin or diabetes medications (like metformin) may occasionally be required.  Some people have continuous high blood sugar levels but not so high that they can be detected as high blood sugar levels. Such people suffer from prediabetes. This condition can have a lethal effect on the person resulting in increased chances of heart disease and strokes. Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetes PatientsIf a person has diabetes, their blood sugar level will fluctuate depending on their age and the time of the day. For instance, blood sugar levels are frequently within the desired range when fasting. The type of food consumed affects blood sugar levels in different ways. It is known that the higher chance of an increase in blood sugar level is just after mealtime, especially when a meal is carbohydrate-rich. The blood sugar levels in children below the age of six are different. They normally have blood sugar levels around 80 to 200 mg/dL. Due to this, parents may need to check their children's blood sugar levels in the middle of the night if they suffer from diabetes or hypoglycemic episodes. On the other hand, teenagers show blood sugar levels between 70 to 150 mg/dL. This is considered a healthy blood sugar level. The teenage years are frequently the most challenging for adolescents with diabetes since treating diabetes demands a lot of responsibility and the hormonal component.  During the time of fasting, blood sugar levels are very low. They become much lower when a person wakes up in the morning because he/she has been starved for around 8 hours. The early morning hours, however, are when many people see a rise in blood sugar levels. If you're an adult who has trouble controlling your blood sugar, your healthcare practitioner can assist you in creating a treatment plan. Apart from the already mentioned blood sugar levels, any fluctuation in the glucose level will result in high or low blood sugar levels. For instance, this chart states that blood sugar levels are high if they are greater than 130 mg/dL before a meal or 180 mg/dL one to two hours after a meal. For many people, symptoms of high blood sugar don't appear until readings reach 250 mg/dL or greater. Signs of Low Blood Sugarwhen a person has lower blood glucose levels, the condition is known as hypoglycemia or low blood sugar. People who suffer from type 1 diabetes inject insulin. If an overdose of insulin or a person has taken fast-acting insulin, he/she has a higher risk of developing low blood sugar. Too much insulin drops blood sugar levels. Improper timing of taking insulin also results in the same condition. Your healthcare professional will explain when and how to check your blood sugar levels and how and when to treat low blood sugar. Less than 70 mg/dL is typically a low blood sugar level. You are at risk if your blood sugar is below 54 mg/dL. In addition, alcohol, certain drugs or drug combinations, endocrine problems, eating disorders, and liver, kidney, or heart diseases can all contribute to low blood sugar levels.  The following list includes some of the most typical signs of low blood sugar:
You may experience some of the early symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as sweating, light-headedness, and dizziness if your blood sugar is low, only by testing your blood sugar using a glucose meter (a glucose monitoring tool) or keeping an eye on it continuously with a glucose monitor like Dexcom G6. If a person has frequent incidents where his blood sugar levels have dropped, it is advised him to carry glucagon when all the time. A family suffering from the same situation should be given training on administering glucose, such as baqsimi nasal spray. It is helpful to avoid unconsciousness. Additionally, suppose the situation is even more serious. In that case, the person is advised to wear an emergency medical alert kit to let the first responder deal with the situation as soon as possible. Signs of High Blood SugarHigh blood sugar is referred to medically as hyperglycemia. A person suffers from hyperglycemia when the insulin levels are dropped or in a situation where the body cannot utilize insulin properly. Various factors are responsible for this condition, including a person suffering from type-1 or type-2 diabetes, depression, stress, anxiety, etc. It is always a good idea to speak with a healthcare physician if you have hyperglycemia or think you might. 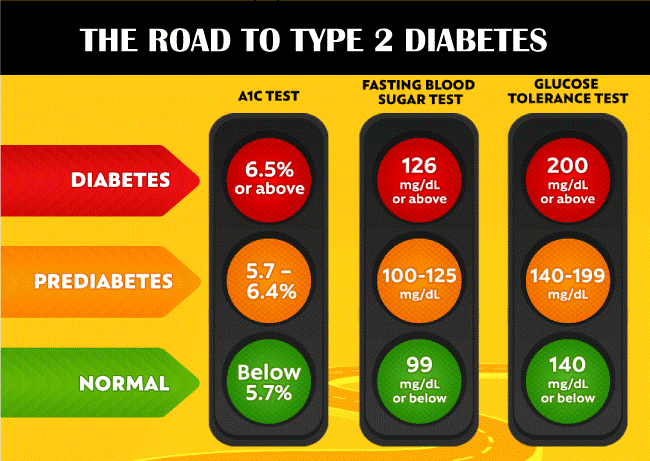 The following are some of the most typical signs of hyperglycemia:
Diabetic ketoacidosis can result from untreated hyperglycemia. In a condition known as ketoacidosis, the body produces waste products known as ketones that can accumulate in the blood and pose a life-threatening threat. The presence of ketones can be determined using a blood or urine test. Ketoacidosis signs and symptoms include:
You'll receive a treatment plan from your doctor that specifies when you need to get emergency medical help. The following lifestyle modifications and medical procedures can help treat hyperglycemia:
Quick Blood Sugar TestSimple finger sticks can be used for this test, which can also be performed at a lab or healthcare provider's office. Alternatively, your doctor may advise that you use a metre and conduct regular tests at home. A CGM allows some people to view their blood sugar levels in real-time. 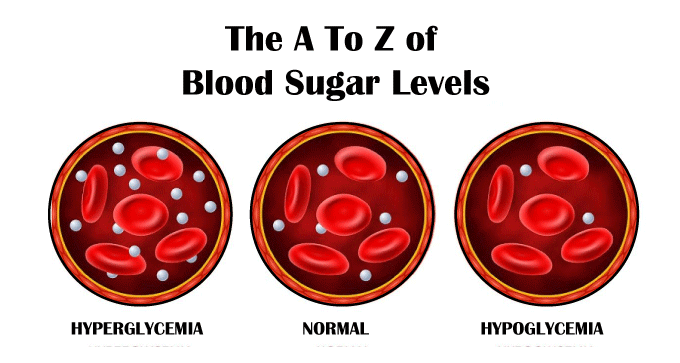 Test for Glucose ToleranceA glucose tolerance test measures your blood glucose levels before and after consuming a sweet beverage. Your fasting blood sugar level will be taken first. After consuming the sweet liquid, your blood sugar will be checked an hour, two hours, and potentially three hours later. 140 mg/dL or less is regarded as normal blood sugar at the 2-hour mark, while 140 to 199 mg/dL denotes prediabetes, and 200 mg/dL or over denotes diabetes. When to Seek Medical AttentionSome medical professionals could ask for a blood sample to check your blood sugar levels. A1C testing, a blood test that gauge's blood sugar control over three months, may also be requested. It's usually a good idea to verify before your appointment because you might need to fast for eight hours to acquire correct test results. If you have diabetes or prediabetes, your doctor can develop a treatment plan for you. 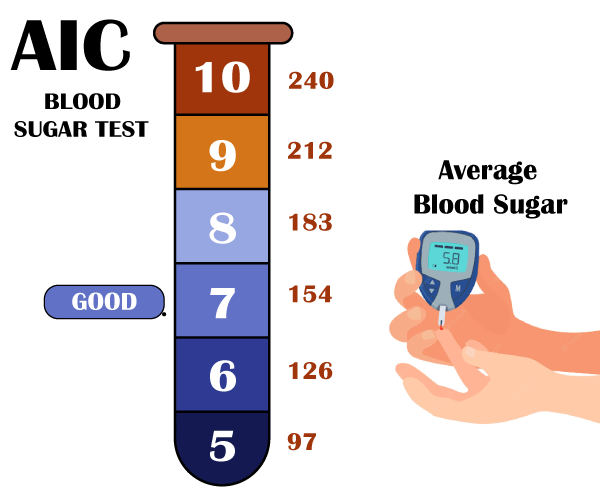 Make sure your treatment plan specifies when you should seek emergency medical attention. Emergency rooms have the tools necessary to manage high blood sugar levels, and they can provide care such as insulin therapy and fluid or electrolyte replenishment. Next TopicBlood Circulation |