C is a general-purpose, structured, procedural, and high-level programming language developed by Dennis MacAlistair Ritchie in 1972 at Bell Laboratories. The successor of the C language was CPL (Combined Programming Language). It is mainly used for system programming such as to develop the operating system, drivers, compilers, etc.
The best-known example of the operating system that was developed using C language is Unix and Linux.
Java is also an object-oriented, class-based, static, strong, robust, safe, and high-level programming language. It was developed by James Gosling in 1995. It is bot compiled and interpreted. It is used to develop enterprise, mobile, and web-based applications.
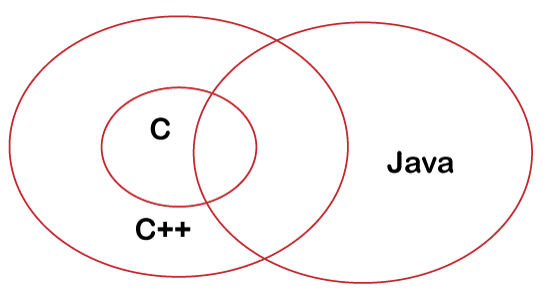
The following figure demonstrates that C++ is based on the C language and Java is based on the C++ and C language.
The languages are based on each other but still, they are different in design and philosophy. The following table describes the major differences between C, C++, and Java. It will help you to select which language you have to learn.
| S.N. |
Basis |
C |
C++ |
Java |
| 1 |
Origin |
The C language is based on BCPL. |
The C++ language is based on the C language. |
The Java programming language is based on both C and C++. |
| 2 |
Programming Pattern |
It is a procedural language. |
It is an object-oriented programming language. |
It is a pure object-oriented programming language. |
| 3 |
Approach |
It uses the top-down approach. |
It uses the bottom-up approach. |
It also uses the bottom-up approach. |
| 4 |
Dynamic or Static |
It is a static programming language. |
It is also a static programming language. |
It is a dynamic programming language. |
| 5 |
Code Execution |
The code is executed directly. |
The code is executed directly. |
The code is executed by the JVM. |
| 6 |
Platform Dependency |
It is platform dependent. |
It is platform dependent. |
It is platform-independent because of byte code. |
| 7 |
Translator |
It uses a compiler only to translate the code into machine language. |
It also uses a compiler only to translate the code into machine language. |
Java uses both compiler and interpreter and it is also known as an interpreted language. |
| 8 |
File Generation |
It generates the .exe, and .bak, files. |
It generates .exe file. |
It generates .class file. |
| 9 |
Number of Keyword |
There are 32 keywords in the C language. |
There are 60 keywords in the C++ language. |
There are 52 keywords in the Java language. |
| 10 |
Source File Extension |
The source file has a .c extension. |
The source file has a .cpp extension. |
The source file has a .java extension. |
| 11 |
Pointer Concept |
It supports pointer. |
It also supports pointer. |
Java does not support the pointer concept because of security. |
| 12 |
Union and Structure Datatype |
It supports union and structure data types. |
It also supports union and structure data types. |
It does not support union and structure data types. |
| 13 |
Pre-processor Directives |
It uses pre-processor directives such as #include, #define, etc. |
It uses pre-processor directives such as #include, #define, #header, etc. |
It does not use directives but uses packages. |
| 14 |
Constructor/ Destructor |
It does not support constructor and destructor. |
It supports both constructor and destructor. |
It supports constructors only. |
| 15 |
Exception Handling |
It does not support exception handling. |
It supports exception handling. |
It also supports exception handling. |
| 16 |
Memory Management |
It uses the calloc(), malloc(), free(), and realloc() methods to manage the memory. |
It uses new and delete operator to manage the memory. |
It uses a garbage collector to manage the memory. |
| 17 |
Overloading |
It does not support the overloading concept. |
Method and operator overloading can be achieved. |
Only method overloading can be achieved. |
| 18 |
goto Statement |
It supports the goto statement. |
It also supports the goto statement. |
It does not support the goto statements. |
| 19 |
Used for |
It is widely used to develop drivers and operating systems. |
It is widely used for system programming. |
It is used to develop web applications, mobile applications, and windows applications. |
| 20 |
Array Size |
An array should be declared with size. For example, int num[10]. |
An array should be declared with size. |
An array can be declared without declaring the size. For example, int num[]. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










