What is the full form of DBT1. DBT: Direct Benefit Transfer DBT stands for Direct Benefit Transfer. The Indian government's attempt to alter how subsidies are transferred is known as Direct Benefit Transfer or DBT. It was introduced on January 1, 2013. This plan or programme aims to set up a Giro system to send benefits to recipients directly through their connected bank accounts. It is thought that depositing subsidies into bank accounts will lessen leaks, fraud, and delays and that the new procedures will boost accountability and transparency. On January 1, 2013, Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) was launched, to improve the government delivery system in welfare schemes by re-engineering the current procedure. This was done for the easier and quicker flow of information and cash and to assure precise beneficiary targeting, de-duplication, and fraud reduction. It was thought conceivable to transit to a system of providing financial benefits directly to the needy thanks to the swift adoption of Aadhaar in the nation. Deployment of DBTThe Planning Commission established the DBT Mission as the focal point for carrying out the DBT programmes. The operation worked until 14.9.2015 after being transmitted to the Bureau of Expenditure on July 23 2013. After 14.9.2015, the DBT Mission and its related matters were moved to the Cabinet Secretariat under the Secretary (Coordination & P.G.). The government launched DBT's first phase in 43 districts, and 78 more communities were eventually included in 27 programmes for the welfare of women, children, and the working class. On December 12, 2014, DBT was further extended throughout the nation.  In 300 designated districts with higher Aadhaar enrolment, they brought seven new scholarship programmes and the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) under DBT. By the office memorandum dated 13.2.2015 and 19.2.2015, they established the Electronic Payment Framework. All Ministries, Departments, and the PSUs affiliated with this Framework must have adhered. It also applies to all Central Sector (C.S.) and Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS) projects. While the initial DBT deployment has addressed some delivery-related challenges and achieved some of its goals, it has also generated a new set of issues that need to be addressed. Officials informed beneficiaries of the need to open and maintain a bank account to implement DBT effectively. Economic inclusion and financial education programmes at the national level get included. Since the inauguration of the PM's Jan Dhan Yojana (PM's People's Wealth Scheme) in August 2014 and the JAM Yojana, the bank-mobile-identification trinity has been implemented to this end. Among the challenges experienced by female beneficiaries in rural locations are tracking deposits, interpreting SMS notifications, knowing the exact amount owed, making sure that the correct amount has been paid, and mobility. Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi claimed that only 15 paise of every rupee spent went to the needy in the 1980s. The Modi administration has argued that every rupee now finds its designated recipient thanks to direct transfers. HistoryThe 2006 Andhra Pradesh smartcard initiative served as a forerunner to DBT. International precedents include Mexico's 2002-launched Oportunidades social aid programme, modelled after the 1997-launched Progresa programme. Similar pilots include Give Directly UCT in Kenya and Bangladesh's Shombhob. A conditional cash transfer programme has also been launched in nations like Turkey, Jamaica, and South Africa. In 1996, Brazil had its initial currency credit transaction. On February 14, 2011, Nandan Nilekani established a task force to make recommendations for developing a system to transfer benefits to recipients directly.  The nodal agency was established as a DBT Mission. It was established under the Planning Commission, moved to the Finance Ministry's Department of Expenditure, and finally became a part of the Cabinet Secretariat. This indicated that DBT was not the purview of a single ministry and that several churches would need to organize their implementation priorities under centralized management. This Direct Benefit Transfer program's primary goal is to restore transparency to the distribution of money supported by the Indian Central Government and put an end to theft. Citizens below the poverty threshold will get benefits or subsidies directly under the DBT system. The creation of the beneficiary list, its digital signature, and the processing of payments into the beneficiary's bank accounts are all done using CPSMS/PFMS. The programme debuted on January 1, 2013, in a few Indian cities. It was facilitated by the JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, and Mobile) trinity. It uses electronic funds transfer services, including National Electronic Funds Transfer and core banking (NEFT). The value of money transfers between F.Y. 2013 and F.Y. 2021 was 21 lakh crore (US$260 billion). The intended beneficiary must have both an Aadhaar number and a bank account to enrol. The person must link their bank account to their Aadhar before connecting it to the desired programme. In addition to submitting numerous documents, some people will need to travel a considerable distance, and they may hesitate for various social and communicational reasons. DBT ProgrammesThere are number of DBT-related programmes and will be 313 schemes in 2021-22 (cash + in kind). On January 1, 2013, DBT operated in 20 districts with seven central sector initiatives. In reality, the rollout could only be managed by 1 section. The government decided to expand DBT to 27 major schemes in 78 more areas of the nation starting on July 1, 2013, following a prime ministerial review. Direct benefit transfer for LPG (DBTL) was formally introduced on June 1, 2013, by Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas M Veerappa Moily in 20 high Aadhaar relevant districts. The Aadhaar-linked bank accounts of consumers would receive direct credit for the LPG cylinder subsidy. As soon as they reserve the first subsidized cylinder before delivery, all Aadhaar-linked residential LPG customers would receive an advance in their bank accounts. The government will pay the next cylinder's subsidy to their bank account when they receive the first subsidized cylinder. They can then use this money to buy the following cylinder at the market price until the annual cap of 12 cylinders is reached. On November 15, 2014, the administration enacted a modified version of the Direct Benefit Transfer of LPG (DBTL) scheme in 54 districts across 11 states. Under this programme, LPG users who haven't yet benefited can get cash subsidies deposited into their accounts to purchase LPG cylinders at market rates. Contrary to the use of DBT in LPG subsidies, the beneficiary's method for obtaining donations while using DBT for food and fertilizer subsidies has differed due to the cash flow to different places. Janani Suraksha Yojana and scholarships accounted for 83 per cent of all transfers through CPSMS, according to an assessment by the Prime Minister's Office on August 5, 2013. The rollout was hampered by a lack of digitized records for schemes that would be connected to DBT. According to the minutes, 56 per cent of the 39.76 lakh beneficiaries who various plans should have covered had bank accounts, and only 25.3% had both bank accounts and aadhaar numbers. Only 9.62 per cent had bank accounts that had been seeded with aadhaar numbers. By May 31, 2016, 74 schemes from 17 ministries of the federal government were under DBT. By August 2019, the government had found 3,486 state/U.T. schemes, and 439 central plans had been added. The DBT website listed 313 CS/CSS from 53 ministries as of March 2022. 2. Department of BiotechnologyIn another scenario, DBT stands for Department of Biotechnology. The Ministry of Science and Technology in India has a department called the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) that manages research and commercialization in the fields of contemporary biology and biotechnology in India. It was established in 1986.  Strategy For National Biotechnology DevelopmentTo support the Mission of developing innovative products, building a solid infrastructure for research and development, commercialization, and empowering human resources scientifically and technologically, stakeholders in the biotechnology and technology areas have made significant investments. 3. Dialectical Behaviour TherapyDBT also stands for Dialectical Behaviour Therapy. The goal of dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), evidence-based psychotherapy, was initially to treat interpersonal issues and personality disorders initially. According to evidence, DBT may help treat mood disorders, suicide ideation and changing behavioural patterns, including self-harm and substance abuse. DBT has developed into a method where the client and therapist combine acceptance- and change-oriented methods akin to the philosophical dialectical process of thesis and antithesis, followed by synthesis. A psychology investigator at the University of Washington named Marsha M. Linehan created this method. 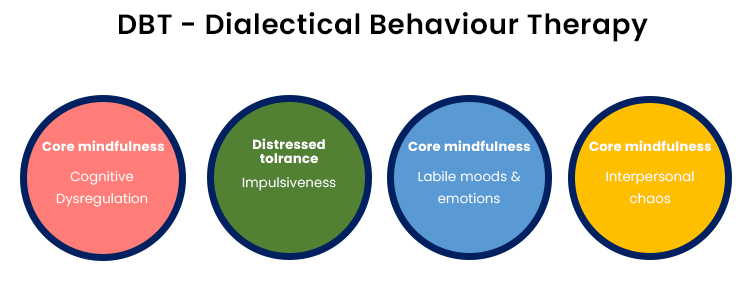 DBT was created to assist individuals in improving their ability to control their emotions and thoughts. This involved learning about the triggers that result in reactive states and assessing and also included which coping mechanisms to use in the flow of events, thoughts, feelings, and behaviours to help avoid unwanted reactions. DBT developed due to several failed attempts to treat clients who were chronically suicidal with the traditional cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) procedures of the late 1970s. There has been successful research into DBT's efficacy in treating other conditions. According to a study, DBT may be able to assist individuals with the signs and behaviours of spectrum mood disorders, including self-harm. Recent research suggests it helps treat drug dependency and sexual abuse survivors. The principles of distress tolerance, acceptance, and mindful awareness are mainly derived from contemplative meditation practice. These are combined with standard cognitive-behavioural approaches for emotion regulation and reality checking in DBT. DBT is the first therapy scientifically shown to be usually helpful in treating borderline personality disorder, and it is based on the biosocial theory of mental disease (BPD). When compared to standard care, the first DBT randomized clinical trial revealed lower rates of suicide thoughts, actions, and admissions to mental hospitals. According to a meta-analysis, DBT had moderate effects on those with BPD. OverviewCognitive-behavioural therapy's "third wave" includes dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), which modifies CBT to help patients manage stress. When treating psychiatric problems, DBT aims to have the patient see the therapist as an ally rather than an enemy. In light of this, the therapist seeks to accept and validate the client's feelings at any given time while educating the client about the mal-adaptiveness of specific emotions and actions and demonstrating other options. To accomplish a "life worth living," as determined by the patient, DBT focuses on the client learning new skills and altering their habits. 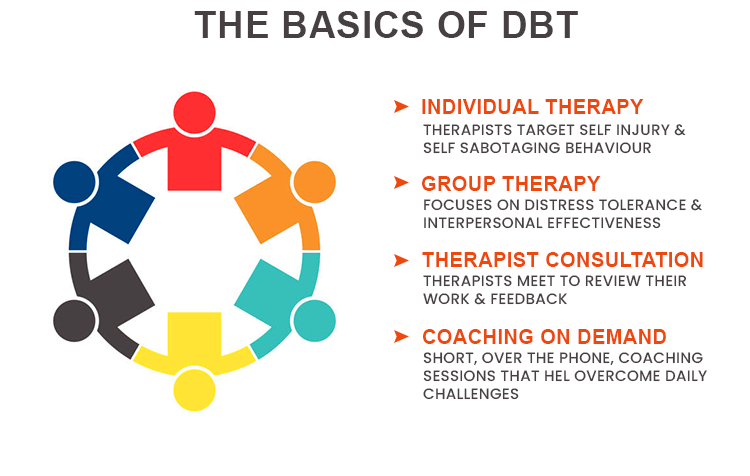 According to the biosocial hypothesis of BPD advocated by DBT, clients with the disorder have a biological propensity for emotional dysregulation, and their social context supports inappropriate conduct. According to the biosocial hypothesis of BPD advocated by DBT, clients with the disorder have a biological propensity for emotional dysregulation, and their social context supports inappropriate conduct. Some clinical settings use DBT skills training alone to achieve therapeutic objectives. The therapy's more significant focus on emotion regulation has made it applicable in new contexts, including assisting parenting. Mindfulness ModulesDBT's concept of "smart mind" combines the two opposites of "reasonable mind" and "emotion mind." Additional details: Mindfulness One of the basic concepts underlying all DBT components is mindfulness. It is a foundation for the other DBT skills because it enables people to accept and tolerate the strong feelings they might experience when questioning their routines or exposing themselves to distressing circumstances. 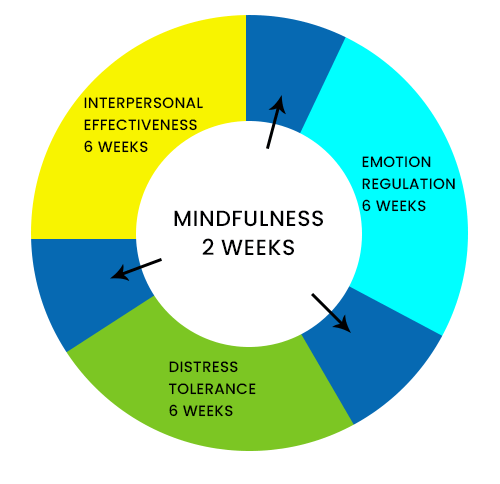 Though the DBT version does not include any theological or metaphysical ideas, the idea of mindfulness and the meditation exercises used to teach it are rooted in traditional contemplative religious practice. In DBT, it is the ability to pay attention to the current moment without passing judgement; it is about living in the moment and ultimately experiencing one's emotions and perceptions living in the moment, fully engaging one's senses and emotions while maintaining perspective. Through the use of their five senses-touch, smell, sight, taste, and sound-people can become more aware of their surroundings through the practice of mindfulness. The accepting principle, often known as "radical acceptance," is crucial to mindfulness. The patient's capacity to accept things and the accompanying emotions depend on their ability to see them without passing judgement. Overall, there is less distress, leading to decreased discomfort and symptomology. DBT as a treatment for CPTSD (Complex post-traumatic stress disorder)The combination of acceptance and goal orientation in DBT as a behaviour modification strategy can empower patients and include them in their treatment. Individuals can be kept from becoming overwhelmed by their traumatized past if they keep their attention on the future and change. Due to the prevalence of numerous traumas in CPTSD, this risk is heightened. Before addressing other parts of a client's treatment, care professionals typically address the client's suicidality. DBT may be an alternative to stabilize suicidality and support other therapy modalities because PTSD might increase a person's risk of experiencing suicidal ideation.  While DBT can be used to treat CPTSD, some detractors contend that it is not noticeably more effective than conventional PTSD treatments. Furthermore, this viewpoint claims that DBT ignores key CPTSD symptoms, including impulsivity, cognitive schemas (repeated, negative beliefs), and emotions like guilt and shame, while decreasing self-harming actions (such as cutting or burning) improving interpersonal functioning. According to the ISTSS, treating CPTSD involves a different approach than treating regular PTSD, which uses a multiphase recovery model rather than concentrating on traumatic memories. The three phases of the suggested multiphase paradigm are social relationships, distress tolerance, and safety. DBT is a therapeutic option because it has four modules (mindfulness, distress tolerance, affect regulation, and interpersonal skills) that generally follow these recommendations. Other criticisms of DBT talk about how prolonged it carries for the remedy to perform. A person seeking DBT might not be able to commit to the necessary number of individual and group sessions, or their insurance might not pay for each. According to research co-authored by Linehan, 56 per cent of women getting outpatient treatment for BPD who had tried suicide in the previous year also satisfied the requirements for PTSD. DBT has started to be used in some contexts to treat traumatic symptoms because features associated with borderline personality disorder and trauma are correlated. Some clinicians combine DBT with additional PTSD treatments like prolonged exposure therapy. For instance, a programme that merged P.E. and DBT would first educate students on how to manage their emotions and practise mindfulness. The person with the disease would then be educated to accept that trauma had occurred and how it might still impact them in the future. Clinical trial participants showed a reduction in symptoms, and during the 12-week experiment, no instances of self-harm or suicidal behaviour were documented. Another justification for using DBT as a trauma treatment is PTSD symptoms, including emotional control and distress. Some PTSD treatments, such as exposure therapy, may not be appropriate for people with limited distress tolerance and emotion regulation. According to the biosocial hypothesis, emotional dysregulation is brought on by a person's increased emotional sensitivity coupled with contextual elements (such as invalidating emotions, ongoing trauma or abuse) and ruminative tendencies (repeatedly thinking about an adverse event and how the outcome could have been changed). These characteristics increase the likelihood of a person engaging in unhealthy coping mechanisms.  DBT can be helpful in these situations since it teaches the proper coping mechanisms and enables the patients to achieve some level of self-sufficiency. The first three DBT modules help people develop their ability to cope with distress and control their emotions, which opens the door to working on symptoms like intrusions, low self-esteem, and interpersonal relationships. It's noteworthy that DBT has frequently been adjusted depending on the target audience. For instance, DBT is changed to include exposure exercises in veteran groups. And take into account insurance coverage and the possibility of traumatic brain damage (TBI) (i.e. shortening treatment). Populations with concomitant BPD may need to stay in the "Establishing Safety" phase for extended periods. The DBT skills training component has significantly improved adolescents' capacity for emotion control and appropriate emotional expression. Adaptations might be made in populations where there is concomitant substance use. For instance, a provider might want to use motivational interviewing techniques (psychotherapy which uses empowerment to inspire behaviour change). We should also provide reference to the extent of substance use. Some people only know how to cope by using drugs or alcohol, so the provider may try to apply skills training before focusing on substance reduction. Before beginning DBT for the trauma, the practitioner may decide to address the substance use if it interferes with treatment compliance or attendance. 4. Data build toolAn open-source command-line tool called DBT aids in the more efficient transformation of data in a warehouse by analysts and developers. It began at RJMetrics in 2016 to provide Stitch with some rudimentary transformation capabilities (acquired by Talend in 2018). Early versions of dbt allowed analysts to participate in the data transformation process using software engineering best practices. DBT has always been an open-source project. On top of DBT Core, the dbt Labs team (previously known as Fishtown Analytics) created a for-profit product in 2018. DBT Labs launched its Series A in April 2020, led by Andreessen Horowitz. DBT Labs announced its Series B funding in November, sponsored by Andreessen Horowitz and Sequoia. And the respective Labs raised its Series C headed in June 2021. By Andreessen Horowitz, Sequoia, and Altimeter. The company raised $222 million for its Series D in February 2022, valued at $4.2 billion. OverviewBy using select statements, analytics engineers can modify data in their warehouses using dbt. Also DBT is designed to alter data already present in a warehouse efficiently; it does not drag or pack data. Instead, it performs the transformation (T) step of the extract, load, and transform (ELT) operations. According to the dbt point of view, it aims to enable analysts to operate more like software engineers. Next TopicFull Form |