Difference Between Conduction Convection and RadiationConduction, convection, and radiation transfer heat differ in how the heat transfer process performs in each of them. The physical transfer of thermal energy in heat between two bodies is known as heat transfer.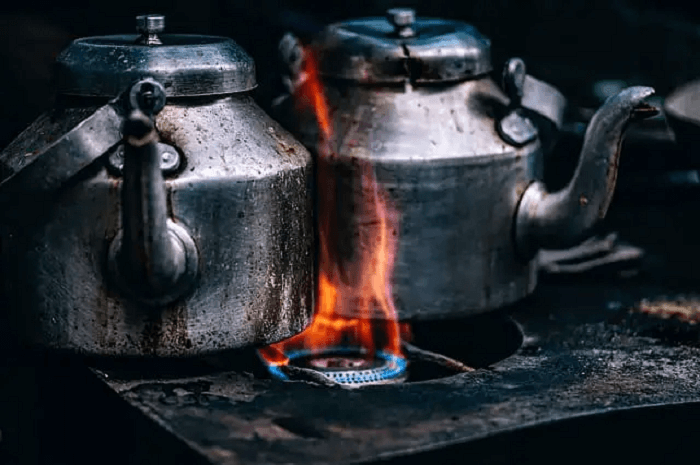  Temperature and heat flow are the essential concepts of heat transfer. Temperature is a measure of the total quantity of thermal energy, and heat flow is a term used to describe the flow of thermal energy. The three methods by that heat may transfer from one object to another are conduction, convection, and radiation. Although these processes are distinct, they can occasionally happen simultaneously. Conduction Definition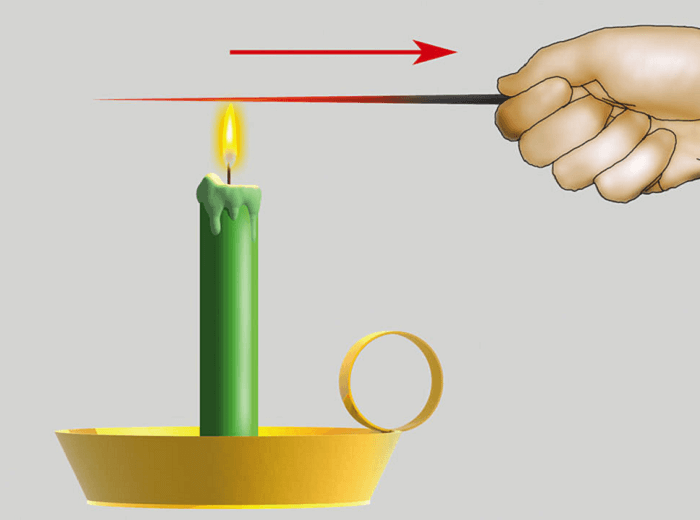 Conduction is the procedure that allows for the direct transport of heat through the material due to the temperature differential between adjacent areas of the item. It occurs when the molecule in a material experience a rise in temperature, which causes furious vibration. They also cause the surrounding molecules to vibrate, which transfers thermal energy to nearby parts of the item. Conduction transfers heat from a hotter item to a cooler one when two things are in direct touch. In addition, conductors make it simple for heat to move through them. Situations when conduction is present, as examples
Conduction-Affecting Elements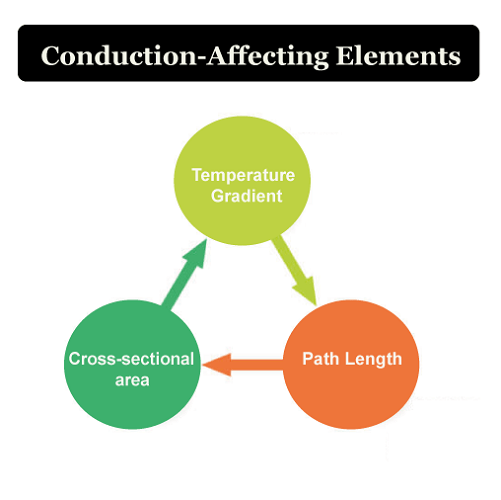 The factors that affect the conduction process are listed below. 1. Temperature Gradient The gradient in temperature directly affects how much heat is transported during conduction. The heat transmission will be more remarkable the more significant the temperature difference. 2. Cross-Sectional Area One critical factor affecting how well heat is transmitted the cross-sectional area. More energy is needed to heat objects with more extensive cross-sectional regions. The heat will be dissipated more quickly when the cross-sectional area is more comprehensive. 3. Path Length The route length refers to the object's height. The transfer of heat should take longer between objects with increased size. Convection Definition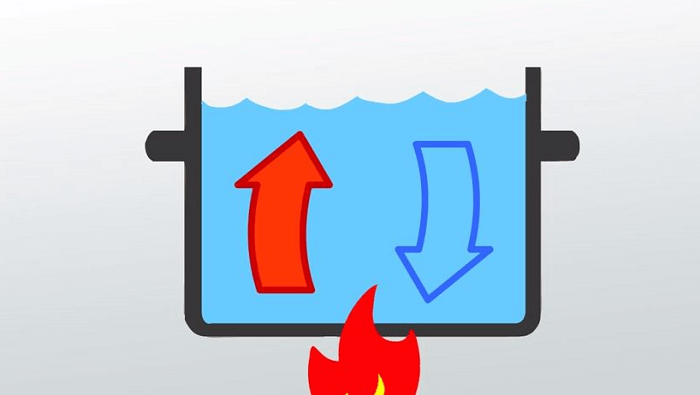 Convection is a scientific term that refers to heat transport that only happens in fluids and involves actual material movement. Any material whose molecules may readily move from one location to another, such as liquid and gas, is called fluid. It occurs voluntarily or even forcibly. Natural convection is supported by gravity, which causes the hotter portion of a substance to increase when it is heated from below. The hotter substance rises because it is less dense and thus has buoyancy. The cold substance replaces it by putting it at the bottom by sinking owing to high density, which, when it gets hot, goes higher, and the process repeats. A substance's molecules spread and move apart during convection due to heating. When convection is done with force, the material is forced to travel higher by any physical means, such as the pump, for instance, a heating system for the air. Kinds of Convection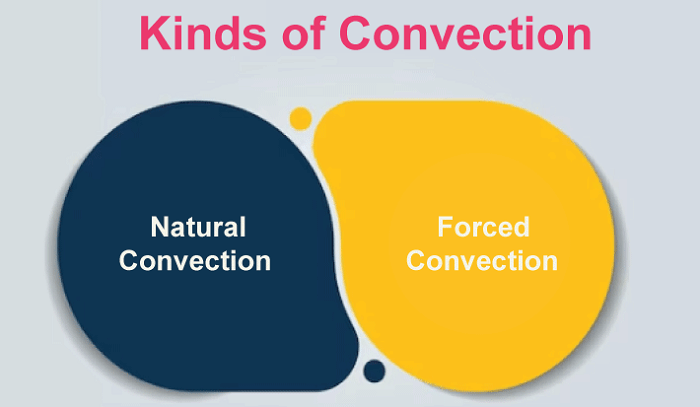 Convection generally is of two kinds 1. Natural Convection 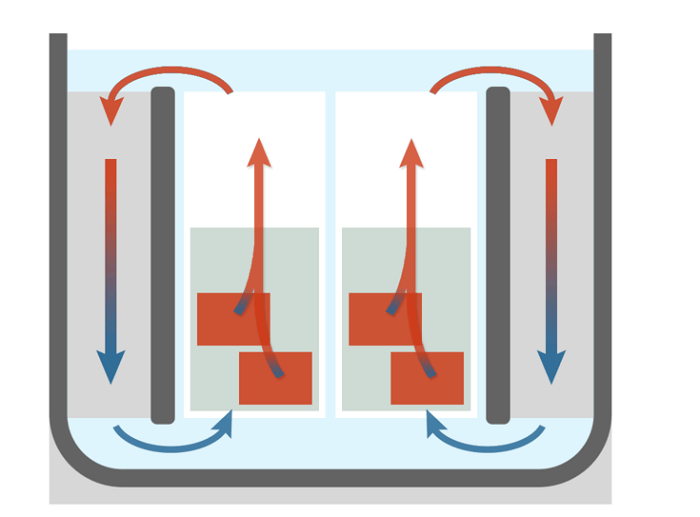 The oceanic winds exhibit this form of convection. It arises as a result of the temperature difference's impact on densities. As a result, buoyant force operates, causing convection. 2. Forced Convection  Using alternative sources such as fans and pumps, forced convection is accomplished. Geysers that are used to heat water are an example of forced convection. Radiation Definition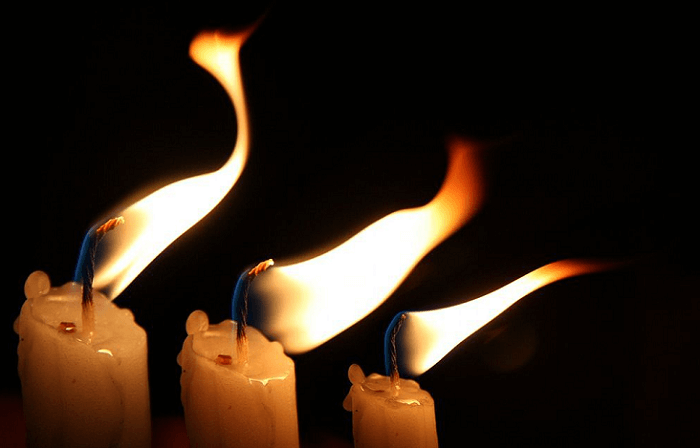 Radiation is the name given to the heat transfer process in which the medium is unnecessary. As it does not require molecules to flow through, it refers to heat transfer in waves. Heat may be transferred between objects without their coming into direct touch. Radiation is the cause of any heat you experience when an object is not directly in contact with you. Moreover, a few surface characteristics significantly impact radiation are color, surface orientation, etc. Radiant energy, the term for electromagnetic waves used in this procedure, conveys power. Thermal energy is often emitted from hot items to colder surroundings. Radiant energy can go from its source to colder surroundings in the vacuum. Despite thousands of kilometers distant, the solar energy we receive from the sun perfectly illustrates radiation. Significant Differences Between Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Conduction, convection, and radiation's significant distinctions from each other are stated as follows.
Important Points to Remember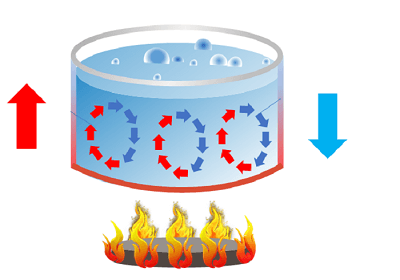
ConclusionHeat transport and the resulting changes are studied in thermodynamics. Conduction means transmitting heat from a hotter to a cooler component. Convection is transferring heat by moving fluid up and down. Heat propagates across void space through processes of radiation. Next TopicDifference between |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India












