Difference Between Ice and SnowIce and Snow are two different forms of water, but significant differences exist between them. Both Ice and Snow have been constructed with the same molecule, but they contain distinct properties and are developed under different conditions.  Ice is a solid form of Some of the significant differences between Ice and Snow are their physical properties. Ice is a solid that is relatively hard and dense. It has a specific gravity of about 0.92, which means it is about 0.92 times as dense as liquid water. Ice can take on many forms, including clear and opaque, depending on how it is formed. For example, when Ice freezes slowly, it can form large, clear crystals; when it freezes quickly, it can form small, opaque crystals.  Snow, on the other side, is another variant of rain that happens when  The density of Snow varies greatly depending on the circumstances under which it was developed. Fresh, powdery Snow is much less dense than older, compacted Snow. In general, the specific gravity of Snow ranges from 0.1 to 0.4, depending on its density and the amount of air trapped within it. This low density makes Snow such a good insulator, which is why animals often burrow into it to escape the cold. Another significant difference between Ice and Snow is their thermal properties. Ice has a greater thermal conductivity than Snow so it can transfer heat more efficiently. Therefore, Ice is used as a coolant system in the refrigeration system. On the other hand, Ice Snow is an excellent insulator and can help maintain a constant temperature in the soil. This is why Snow can benefit plants during the winter months, as it helps protect their roots from extreme temperature fluctuations. The formation of Ice and Snow also differs. Ice is formed when liquid water freezes due to a decrease in temperature, while Snow is formed when water vapor freezes into ice crystals in the atmosphere. The humidity and temperature conditions necessary for the formation of Ice and Snow are also different. Ice can form below 0 degrees Celsius, while Snow requires a combination of low temperatures and high humidity. The properties of Ice and Snow also affect their uses. Ice is commonly used in refrigeration systems, as a coolant in engines, and in the production of ice sculptures. Snow is used in winter sports, such as skiing and snowboarding, and as a source of water in areas where water is scarce. Additionally, Snow can be used for building insulation and producing snow cones and other treats. Ice and Snow also have different effects on the environment. Ice can cause damage to buildings and roads due to its weight and hardness, while Snow can provide insulation for plants and animals during the winter months. Ice and Snow play a vital role in the global water cycle, as they can store water in its frozen form and release it into the environment as they melt. However, the melting of ice caps and Snow due to climate change. Differences Between Ice and Snow in the Tabular Form
Next TopicDifference between |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India
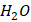 that develops below zero degrees Celsius. It is produced when liquid water freezes due to a reduction in temperature. Ice can be observed in the shape of ice cubes, glaciers, and frozen lakes. The molecular structure of Ice is made up of tightly packed water molecules in a crystalline lattice, which gives it its characteristic hardness.
that develops below zero degrees Celsius. It is produced when liquid water freezes due to a reduction in temperature. Ice can be observed in the shape of ice cubes, glaciers, and frozen lakes. The molecular structure of Ice is made up of tightly packed water molecules in a crystalline lattice, which gives it its characteristic hardness.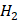 O vapor in the atmosphere freezes into ice crystals. It is developed in the clouds and transcends to the ground as snowflakes. Snowflakes are formed when water vapor freezes around a nucleus, such as a dust particle or a tiny ice crystal. The molecular structure of Snow is similar to that of Ice, but it is much less dense and contains more air pockets. This is why Snow is often considered a "porous" material.
O vapor in the atmosphere freezes into ice crystals. It is developed in the clouds and transcends to the ground as snowflakes. Snowflakes are formed when water vapor freezes around a nucleus, such as a dust particle or a tiny ice crystal. The molecular structure of Snow is similar to that of Ice, but it is much less dense and contains more air pockets. This is why Snow is often considered a "porous" material.











