Difference Between Polar and Non-Polar MoleculesMolecules are the basic units of matter composed of two or more chemically bonded atoms. It contains the types of particles that determine the chemical properties of a molecule and how those atoms are arranged and bonded to each other. An important molecule characteristic is its polarity, which refers to the unequal distribution of electrical charge within the molecule. Molecules can be classified as- polar or non-polar based on their polarity. 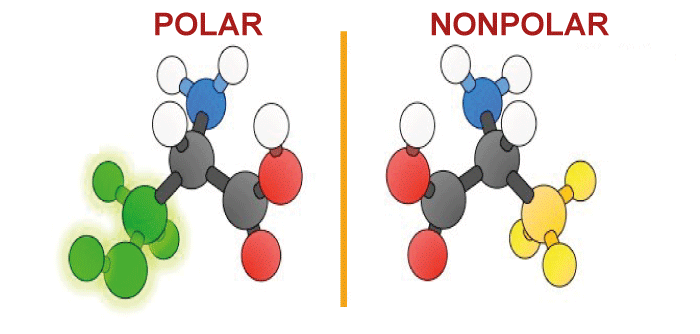 Polar MoleculesPolar molecules are those that exhibit a net dipole moment, which denotes an uneven distribution of electrical charges inside the molecule. This happens when the molecules' atoms exhibit differing electro-negativities, a property that describes an atom's capacity to draw electrons into a chemical connection. A dipole moment develops within a molecule due to the partial positive and partial negative charges created when atoms with differing electro-negativities link together. Water can be an example of a polar molecule. Since the hydrogen atoms in water are more electro-negative than the oxygen atoms, there is a partial charge near the hydrogen atoms and a partial charge near the oxygen atoms. Water is a polar molecule because of the unequal distribution of its charges, which creates a net dipole moment. Non-Polar MoleculesNon-polar molecules are those that have an equitable distribution of electrical charge throughout the molecule and no net dipole moment. This happens when the molecules' atoms share identical electrons in covalent bonds due to comparable electro-negativities. Gases like oxygen and nitrogen and organic molecules like methane (CH4) and benzene are examples of non-polar molecules (C6H6). Non-polar molecules have a limited solubility in water as well as other polar solvents, which is one characteristic that unites them. This is because non-polar molecules cannot engage in hydrogen bonding interactions with the partial charges in water since there isn't a dipole moment. Considering the details mentioned above, the following are some of the primary differences between polar and non-polar molecules:
ConclusionIn conclusion, the existence or lack of a dipole moment, which determines whether a molecule is polar or non-polar, is caused by the even or uneven distribution of electrons inside the molecule. Chemistry, physics, biology, and other scientific fields benefit from understanding how molecules' polarity affects how they interact with one another and their surroundings. Next TopicDifference Between |

We provides tutorials and interview questions of all technology like java tutorial, android, java frameworks
G-13, 2nd Floor, Sec-3, Noida, UP, 201301, India












