Operators in groovyIn groovy, operators are symbols which are used to tell the compiler to perform specified operations. Following are the operators in groovy:
Arithmetic operatorArithmetic operators are the basic mathematical operators, which are used to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, Remainder and Power. Example 1:Output: 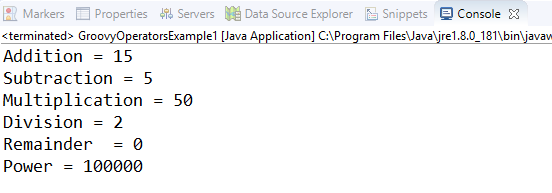 In groovy, we also have some functions which are used to perform Arithmetic operations like plus, minus, intdiv and power. The use of these functions are shown in the example which is given below. Example 2:Output: 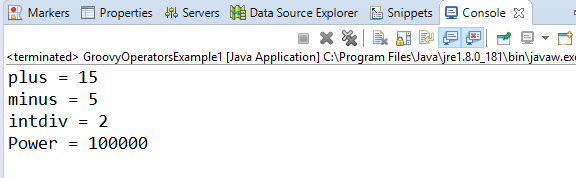 Unary operatorsIn groovy, Unary operators require only one operator to perform the operation. Unary operators are used to perform the operations such as increment/decrement, negating, and inverting the values of a Boolean. Example 3:Output: 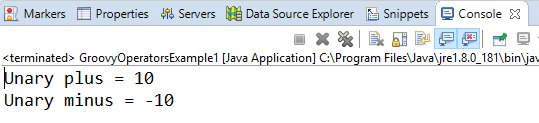 Example 4:Output: 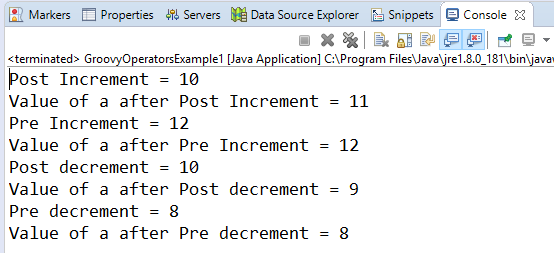 Assignment arithmetic operatorsIn groovy, assignment arithmetic operators are used to assign a new value to the variable. Example 5:Output: 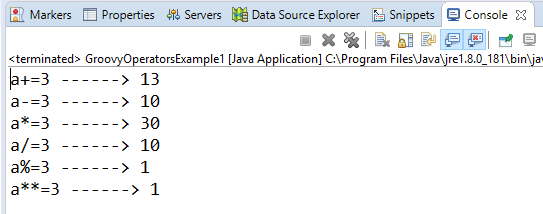 Relational operatorsIn groovy, relational operators are used to compare two objects to check wether they are same or different or one is greater than, less than or equal to other object. Example 6:Output: 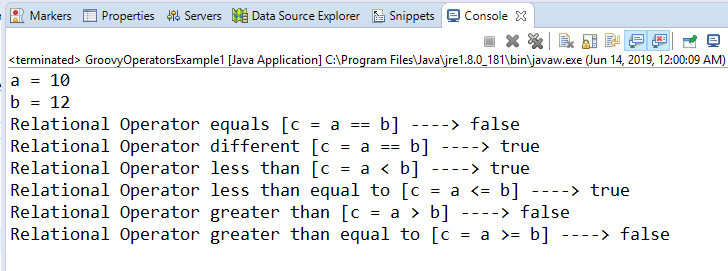 Logical operatorsIn groovy, there are 3 logical operators for Boolean expression, and these operators are AND(&&), OR(||) and NOT(!) Example 7:Output: 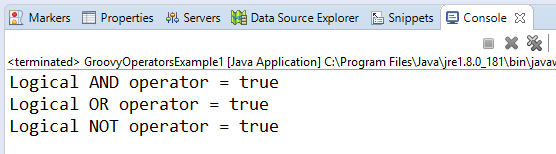 Note: In groovy, logical "not" is having a higher priority as compared to the logical "and".Example 8:Output: 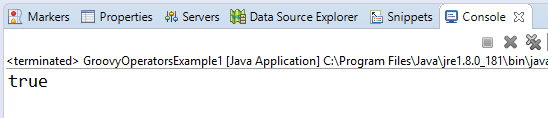 Note: In groovy, logical "and" is having a higher priority as compared to the logical "or".Example 9:Output: 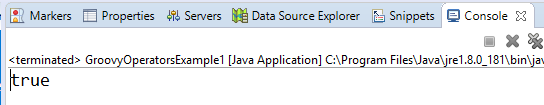 Bitwise operatorsIn groovy, Bitwise operators are used for operating on binary digits or bits of an integer. Example 10:Output: 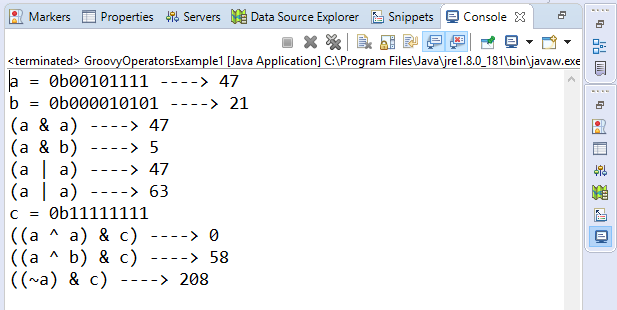 Example 11:Output: 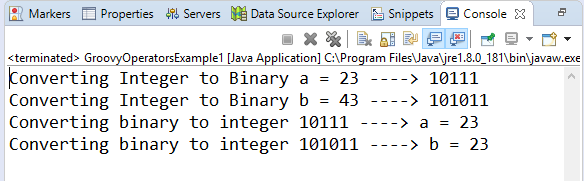 Conditional operatorsIn groovy, there are three types of conditional operators they are as follow:
In groovy, "not" operator is used invert the result of the Boolean expression. Example 12:Output: 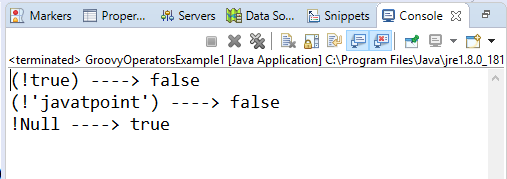
In groovy, Ternary Operator is the shortcut of if/else Example 13:Output: 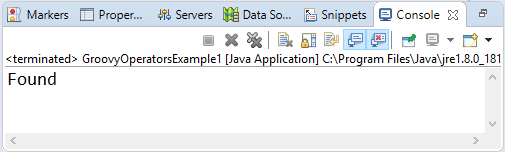
In groovy, Elvis operator is a shorthand property of the ternary operator. It only returns when a value is true. Example 14:Output: 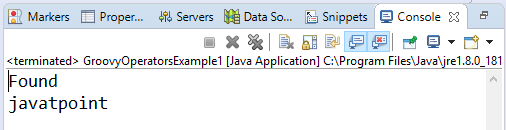 Next TopicGroovy Decision Making |