Introduction to Color SpacesColor spaces are the mathematical representation of a set of colors. There are many color models. Some of them are RGB, CMYK, YIQ, HSV, and HLS, etc. These color spaces are directly related to saturation and brightness. All of these color spaces can be derived using RGB information using devices such as cameras and scanners. RGB Color SpaceRGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. This color space is widely used in computer graphics. RGB are the main colors from which many colors can be made. RGB can be represented in the 3-dimensional form: 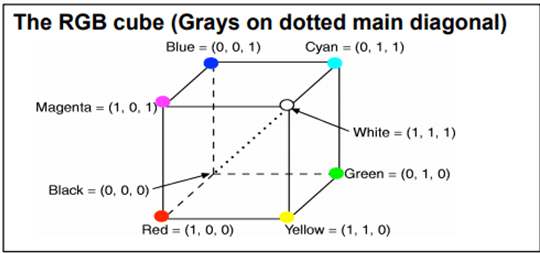 Below table is 100% RGB color bar contains values for 100% amplitude, 100% saturated, and for video test signal. 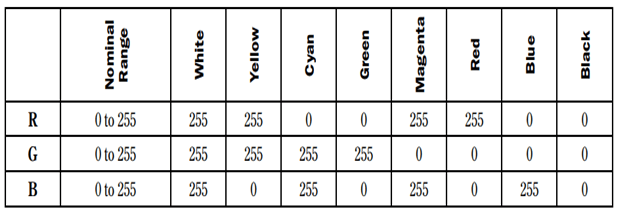 CMYK Color ModelCMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow and Black. CMYK color model is used in electrostatic and ink-jet plotters which deposits the pigmentation on paper. In these model, specified color is subtracted from the white light rather than adding blackness. It follows the Cartesian coordinate system and its subset is a unit cube. 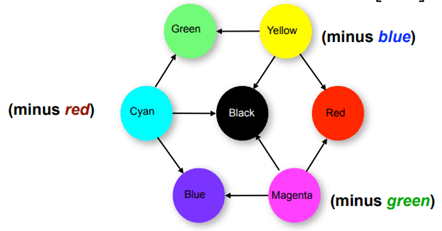 HSV Color ModelHSV stands for Hue, Saturation, and Value (brightness). It is a hexcone subset of the cylindrical coordinate system. The human eye can see 128 different hues, 130 different saturations and number values between 16 (blue) and 23 (yellow). 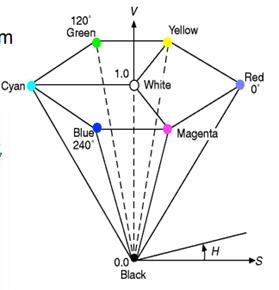 HLS Color ModelHLS stands for Hue Light Saturation. It is a double hexcone subset. The maximum saturation of hue is S= 1 and L= 0.5. It is conceptually easy for people who want to view white as a point. 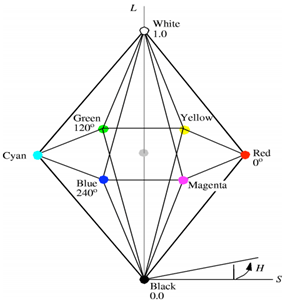 Next TopicIntroduction to JPEG Compression |