Lead Time Calculation in ExcelProjects are focused on providing the client with excellent products and services. The duration of these elements' performance largely determines their quality. In the production sector, this duration is known as the Lead Time. For the process as a whole, lead time calculation is crucial. This post will review two examples of how to compute lead time in Excel. We must first thoroughly understand lead times and their many sorts. Let's dive right into the article without more ado. Lead time: What Is It?The time between a procedure's beginning and end is known as lead time. In more detail, it's the duration needed to produce a good or service a customer wants. The manufacturing sector, supply chain, & project management are the main areas where lead time is utilised. The following is the standard formula for figuring out lead time: Lead Time: End Date - Start Date Varied industries have varied average lead times. These discrepancies arise based on how long each step takes to do the activity. For instance, a customer's order placement and delivery lead time is shorter than a retailer's order purchase and delivery lead time straight from the factory. Lead time is required to set up work and give clients a deadline for getting the desired product. Lead time is also crucial in estimating the time needed for preprocessing, processing, and postprocessing. Lead Time TypesLet's go over the many sorts of lead time now that we are familiar with its details. Lead time is available in four distinct industries. They are as follows:
It is the period between an order being placed and its fulfilment by the client. Several factors affect the customer lead time, including the manufacturing process, delivery methods, and any other cause of delay.
The amount of time needed to purchase an item and then use it to produce a product is known as the material lead time. The length of lead time is influenced by the supplier's lead time, the hours of transportation, and the delay in receiving materials.
It is the time needed to create a product after obtaining all necessary components. The industrial processes, the quantity of labour on hand, and equipment failure may impact it.
The cumulative lead time is the time needed to produce a product. This procedure involves both active manufacturing and labour- or material-assembling time. Cycle Time Compared to Lead TimeNaturally, the subject of what cycle time is coming up while discussing lead time. These two phrases are often confused. However, they are very different from one another. The time it takes to finish a product from the start is called its cycle time. It is only quantified throughout the manufacturing process. On the other hand, lead time refers to the amount of time needed from the moment an order is placed until it is correctly delivered. Two Appropriate Examples of How to Determine a Lead Time through ExcelLet us examine a few cases to gain a deeper understanding of lead time. 1. Lead Time Estimator in Excel for Manufacturers From the perspective of a manufacturer, let us explain the wait time. In this example, we will compute the manufacturing lead time by considering every component needed for the entire process.
=D5-C5 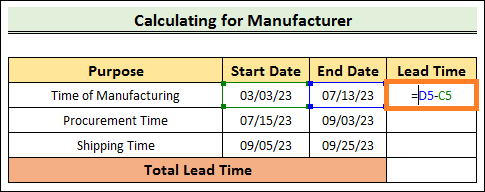
=SUM(E5:E7) 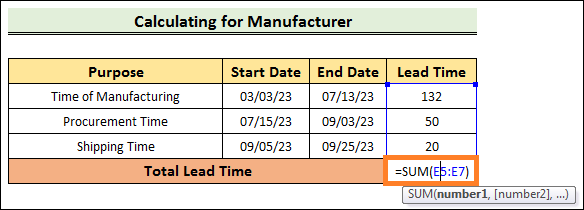
2. Determine the Lead Time for Retailers Using Excel Now, let's look at another lead time calculation. We'll talk about it from a retailer's point of view this time. Follow the steps below to complete the task.
=D5-C5 
=SUM(E5:E7) 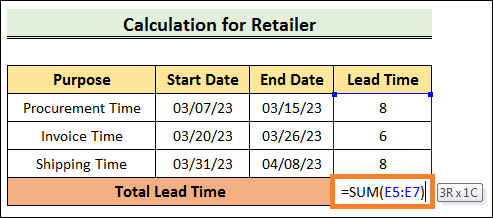
Ultimately, it is evident that the Lead Time varies according to the type, method, and constituents. Consequently, we discovered that the manufacturing lead period is longer than the lead time for buying it from a merchant. Next TopicOutliers Excel |