Modulation in Mobile ComputingModulation is a process of mixing signals with a sinusoid to produce a new form of signals. The newly produced signal has certain benefits over an un-modulated signal. Mixing of low-frequency signal with a high-frequency carrier signal is called Modulation. In other words, you can say that "Modulation is the process of converting one form of signals into another form of signals." For example, Analog signals to Digital signals or Digital signals to Analog signals. Modulation is also called signal modulation. Example: Let's understand the concept of signal modulation by a simple example. Suppose an Analog transmission medium is available to transmit signals, but you have a digital signal that needs to be transmitted through this Analog medium. So, to complete this task, you have to convert the digital signal into an analog signal. This process of conversion of signals from one form to another form is called Modulation. Need for Modulation/ Why Use Modulation?The baseband or low-frequency signals are not such strong and compatible signals that can be used for direct transmission. To make these signals travel longer distances, we have to increase their strength by modulating them with a high-frequency carrier wave. This process doesn't affect the parameters of the modulating signal. Modulation is used to make the message carrying signal strong to be transmitted over a long distance and establish a reliable communication. A high-frequency signal can travel up to a longer distance without getting affected by external disturbances. In Modulation, these high-frequency signals are used as a carrier signal to transmit the message signal. This process is called Modulation. In Modulation, the carrier signals' parameters are changed according to the instantaneous values of the modulating signal. Another reason to modulate a signal is to allow a smaller antenna as we know that a low-frequency signal would need a huge antenna. An antenna needs to be about 1/10th the length of the wavelength of the signal to be efficient. Modulation converts the low-frequency signal into a much higher frequency signal, which has much smaller wavelengths and allows a smaller antenna. Advantages of ModulationFollowing is the list of some advantages of implementing Modulation in the communication systems:
Types of ModulationPrimarily Modulation can be classified into two types:
Digital ModulationDigital Modulation is a technique in which digital signals/data can be converted into analog signals. For example, Base band signals. Digital Modulation can further be classified into four types:
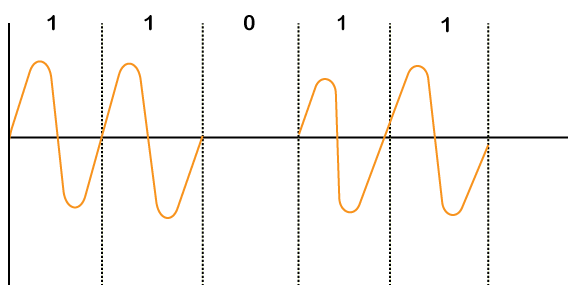
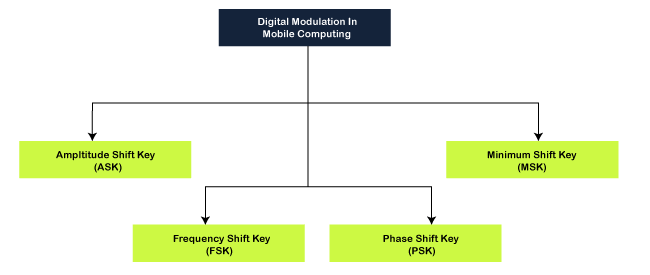 Amplitude Shift Key (ASK) Modulation
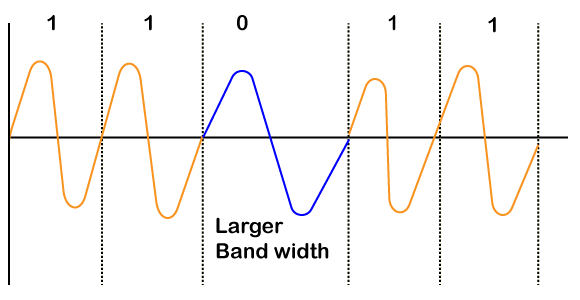
 Minimum Shift Key (MSK) Modulation
Frequency Shift Key (FSK) Modulation
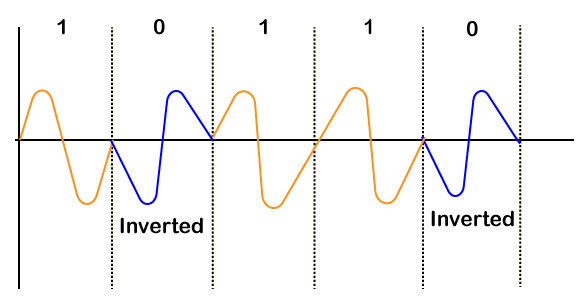
 Phase Shift Key (PSK) Modulation
 Analog Modulation in Mobile ComputingAnalog modulation is a process of transferring analog low-frequency baseband signal such as an audio or TV signal over a higher frequency carrier signal such as a radio frequency band. Baseband signals are always analog to this modulation. In other words, you can say that "Analog Modulation is a technique which is used in analog data signals transmission into digital signals." An example of Analog Modulation is Broadband Signals. There are three properties of a carrier signal in analog modulation i.e., amplitude, frequency and phase. So, the analog modulation can further be classified as:
Difference between Digital and Analog ModulationBoth digital and analog modulation are used to vary or transform signals from one for to another, but the difference is that an analog-modulated signal is demodulated into an analog baseband waveform. On the other hand, in digital modulation, a digitally modulated signal contains discrete modulation units, called symbols, that are interpreted as digital data. Amplitude ModulationAmplitude modulation or AM is a modulation technique that is used in electronic communication. It is most commonly used for transmitting messages with a radio carrier wave. It varies the instantaneous amplitude of the carrier signal or waves according to the message signal's instantaneous amplitude. If we denote the message signal as m(t) and c(t)= Acoswct, then amplitude modulation signal F(t) will be written as: F(t)= Acoswct+m(t) coswct F(t)=[A+m(t)] coswct 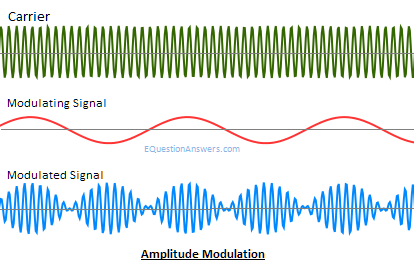 History of Amplitude modulation Amplitude modulation was the earliest modulation technique used for transmitting audio in radio broadcasting. It was developed during the first quarter of the 20th century and was based on the Roberto Landell De Moura and Reginald Fessenden's radiotelephone experiments proposed in 1900. Advantages of Amplitude Modulation
Disadvantages of Amplitude Modulation
Usage of Amplitude Modulation Amplitude Modulation is used in AM radio communication. AM radio broadcast is an example of Amplitude Modulation. Frequency ModulationFrequency Modulation or FM is the process of encoding the information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. It varies the instantaneous frequency of the carrier signal according to the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. If we denote the message signal as m(t) and c(t)= Acoswct, then Frequency modulation signal F(t) will be written as: F(t)= Acos(wc t+kf ∫m(α)dα) 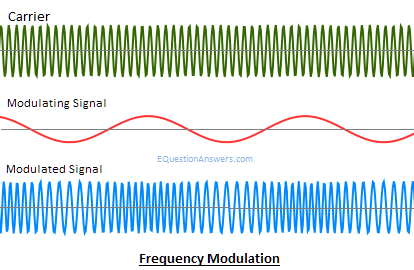 Advantages of Frequency Modulation
Disadvantages of Frequency Modulation
Usage of Frequency Modulation The main example of Frequency Modulation is FM radio broadcasting. Phase modulation (PM)Phase modulation or PM is the technique of varying the carrier signal's instantaneous phase according to the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal. It encodes the message signal as changes occurred in the instantaneous phase of a carrier signal. If we denote the message signal as m(t) and c(t)= Acoswct, then Phase modulation signal F(t) will be written as: F(t)= Acos(wct+kpm(t)) 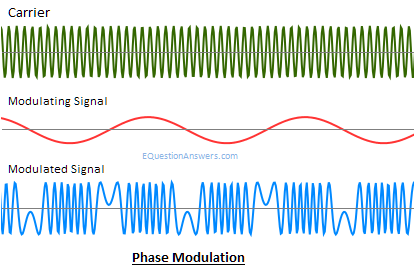 Advantages of Phase modulation
Disadvantages of Phase modulation
Usage of Phase modulation Phase Modulation is mainly used in Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. Next TopicMinimum Shift Key Modulation |