MySQL Natural JoinWhen we combine rows of two or more tables based on a common column between them, this operation is called joining. A natural join is a type of join operation that creates an implicit join by combining tables based on columns with the same name and data type. It is similar to the INNER or LEFT JOIN, but we cannot use the ON or USING clause with natural join as we used in them. Points to remember:
Syntax:The following is a basic syntax to illustrate the natural join: In this syntax, we need to specify the column names to be included in the result set after the SELECT keyword. If we want to select all columns from both tables, the * operator will be used. Next, we will specify the table names for joining after the FROM keyword and write the NATURAL JOIN clause between them. Natural Join ExampleLet us understand how natural join works in MySQL through examples. First, we will create two tables named customer and balance using the below statements: Next, we will fill some records into both tables using the below statements: Next, we will execute the SELECT statement to verify the table data: 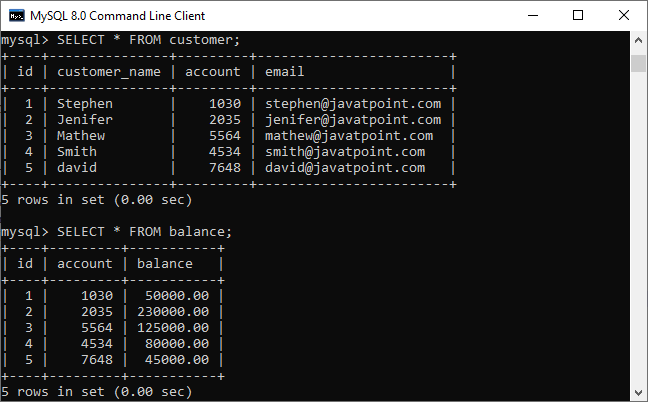 Now, we will see the condition that fulfills the criteria for natural join. We can do this by examining the table structure using the DESCRIBE statement. See the below image: 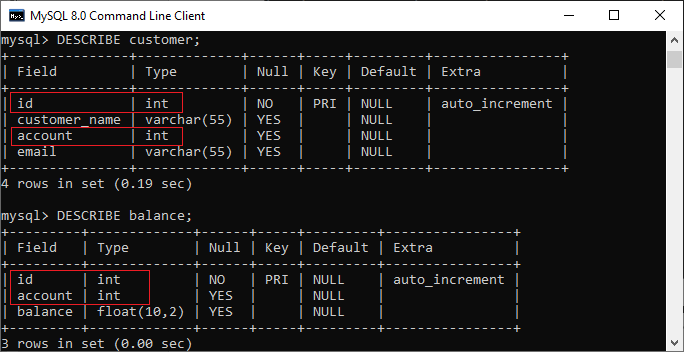 In this image, we can see that column names id and account and its data types are the same that fulfill the natural join criteria. Hence we can use natural join on them. Execute the below statement for joining tables using natural join: We will get the following result: 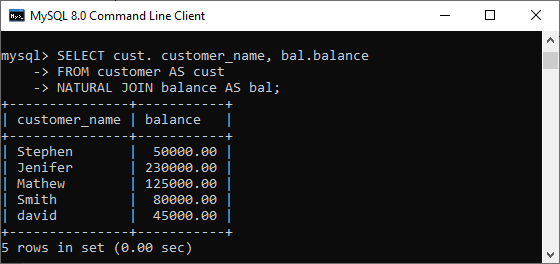 We can do the same job with the help of INNER JOIN using the ON clause. Here is the query to explain this join: After successful execution, we will get the same result as the natural join: 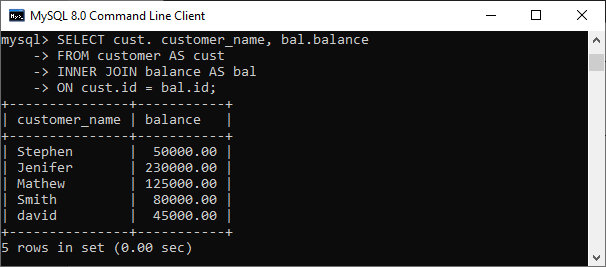 Now, we will use (*) in the place of column names as follows: Suppose we use the asterisk (*) in the place of column names, then the natural join automatically searches the same column names and their data types and join them internally. Also, it does not display the repeated columns in the output. Hence, we should get the below output after executing the above statement: 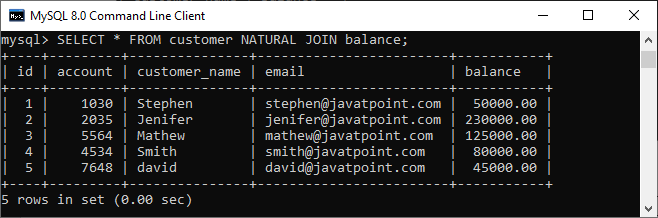 Natural Join with WHERE ClauseThe WHERE clause is used to return the filter result from the table. The following example illustrates this with the natural join clause: We will get the following result where customer information is displayed whose account balance is greater than 50000. 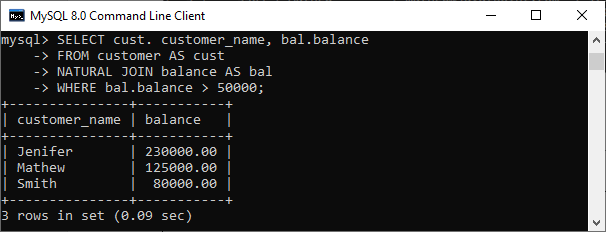 Natural Join Using Three TablesWe know that natural join can also perform a join operation on more than two tables. To understand this, we will use the syntax as follows: Let us create another table named cust_info using the below statement: Then, we will fill records into this table: We can verify the data using the SELECT statement. See the below image: 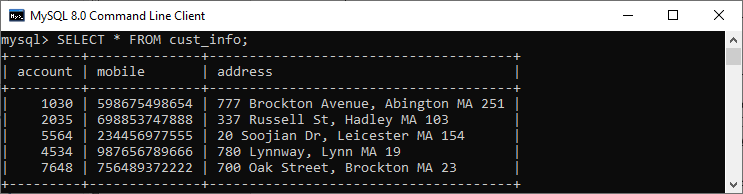 To join three tables using natural join, we need to execute the statement as follows: It will give the below result. Here we can see that the account number is present in all three columns but arrived only once in the output that fulfills the natural join criteria. 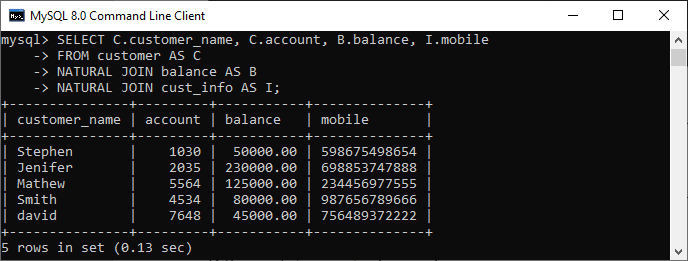 Difference between Natural Join and Inner Join
Next TopicLeft Join vs Right Join |