Oracle GROUP BY ClauseIn Oracle GROUP BY clause is used with SELECT statement to collect data from multiple records and group the results by one or more columns. Syntax: Parameters:expression1, expression2, ... expression_n: It specifies the expressions that are not encapsulated within aggregate function. These expressions must be included in GROUP BY clause. aggregate_function: It specifies the aggregate functions i.e. SUM, COUNT, MIN, MAX or AVG functions. aggregate_expression: It specifies the column or expression on that the aggregate function is based on. tables: It specifies the table from where you want to retrieve records. conditions: It specifies the conditions that must be fulfilled for the record to be selected. Oracle GROUP BY Example: (with SUM function)Let's take a table "salesdepartment" Salesdepartment table: 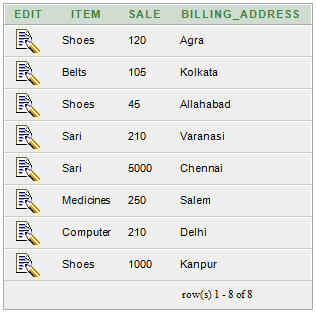 Execute this query: Output 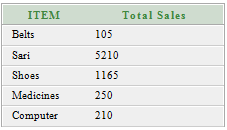 The above example will show the total sales of every individual item. Oracle GROUP BY Example: (with COUNT function)Let's take a table "customers" Here we are creating a table named customers. This table doesn't have any primary key. Customer table: 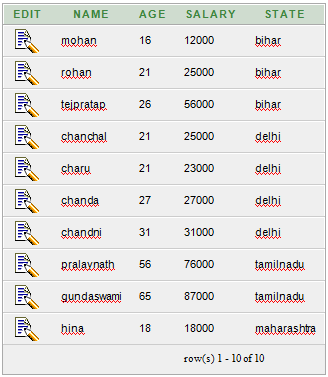 Execute this query: Output: 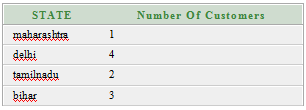 Oracle GROUP BY Example: (with MIN function)Let?s take a table "employees" Employees table: 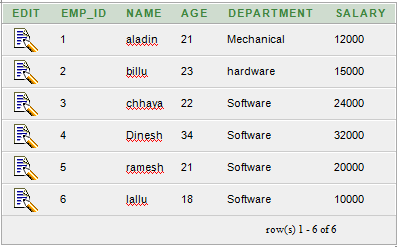 Execute this query: Output: 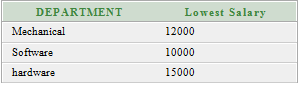 Oracle GROUP BY Example: (with MAX function)In this example, we are using "employees" table that is given above. Execute this query: Output:  Next TopicOracle HAVING Clause |