PowerShell Get-Date FormatIn this article, we will discuss and use PowerShell's Get-Date Format (or Date Format) command. Date and times properties are used several times throughout the PowerShell scripts. Using the Get-Date cmdlet, we can retrieve the current date of our machine. The default format of date is defined on the local system on which we run the command. There are several formats and parameters are used with the Get-Date command. Here, we will only focus on the formatting and display the different date results. Before performing all the Get-Date cmdlet operations on the PowerShell, we must know how to start the PowerShell tool (application). Start PowerShell as an AdministratorThere are various ways to start PowerShell as an Administrator; some of the basic ways are mentioned below: 1. Run PowerShell as an Administrator using Windows's search barStep 1: Windows 10 operating system comes with a search field in the taskbar. Point the cursor in the search field and type "powershell" (or PowerShell). 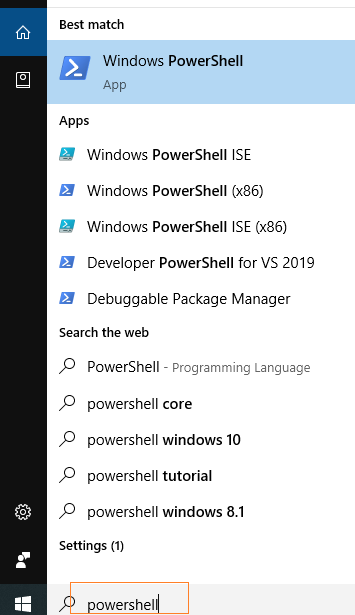 Step 2: Based on the search result, right-click on the Windows PowerShell and Run as Administrator. It will take you to Windows PowerShell's as administrator mode. 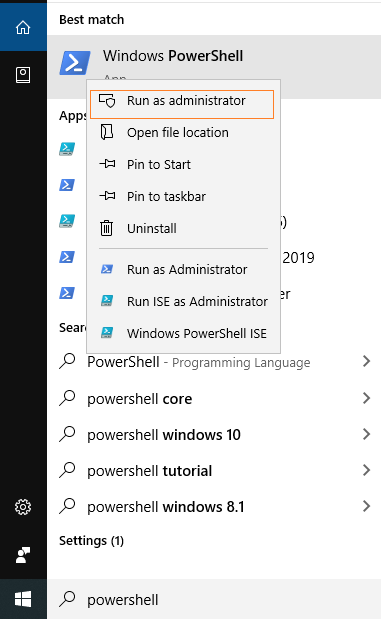 2. Run PowerShell as an Administrator using Run windowStep 1: Press the Windows + R keys simultaneously, and it will open a Run dialog box. Now, type the PowerShell in the Run dialog box and click on the OK button. 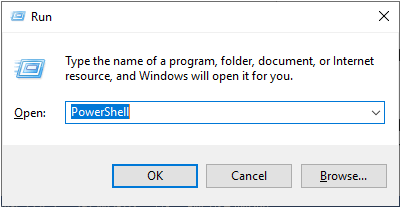 Step 2: Step 1 opens the normal PowerShell windows for the current user. Now, on the PowerShell windows, type the command start-process powershell -verb runas and press the "enter" key. 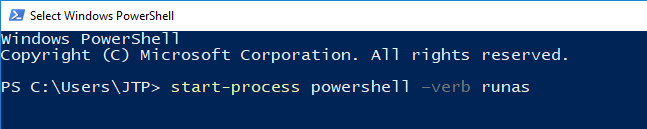 Step 3: The above command asks you to open Windows PowerShell as an administrator mode; click OK to allow, and it will bring the Windows PowerShell to the administrator.  Date Formatting ParametersFollowings are the different types of date format in PowerShell:
When to use Get-DateThe Get-Date command returns a DateTime object that shows the current date or date you specify on your local device. Let's see the default format of the system when we use the Get-Date command.  The Get-Date command returns a date and time value in string type of various UNIX and .NET formats and moves the string to other cmdlets. The format of output shown on your shell's screen is based on your formatted computer settings. To view your device date settings, use the (Get-Culture).DateTimeFormat command; it will return different date and time formats. 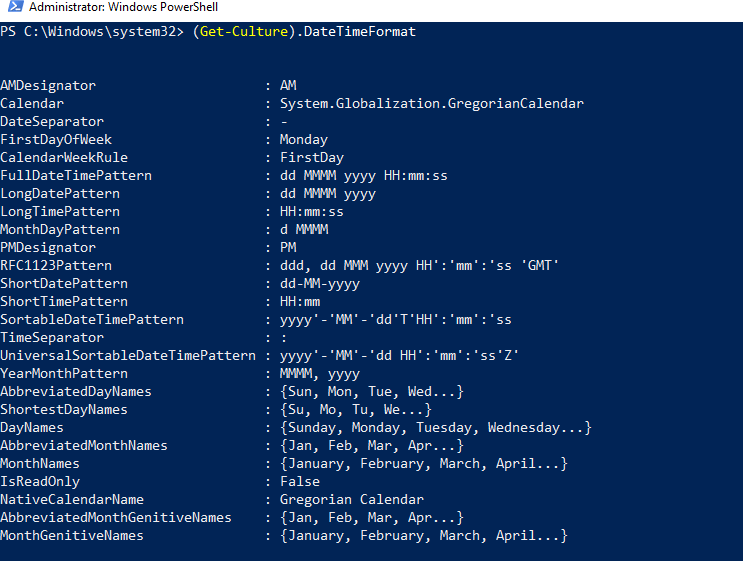 How to use the Get-Date commandThe command Get-Date returns the current date and time of the system, and the result is shown in the form of long-date and long-time formats.  If we use a Format-List cmdlet with Get-Date, we will see the full information that returns various dates and time formats. The command Get-Date returns a DateTime object. Let see the output of using the Get-Date | Format-List cmdlet: 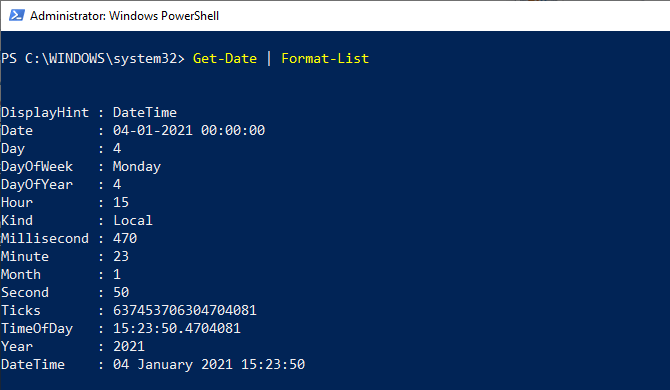 DisplayHintThe DisplayHint parameter defines the type of information we want to display on the screen. This parameter also returns the DateTime object; however, it has three different types of formats, including Date, Time, and DateTime. The -DisplayHint parameter uses anyone from Date, Time, or DateTime at a time.
Let see the output of using the followings cmdlets: 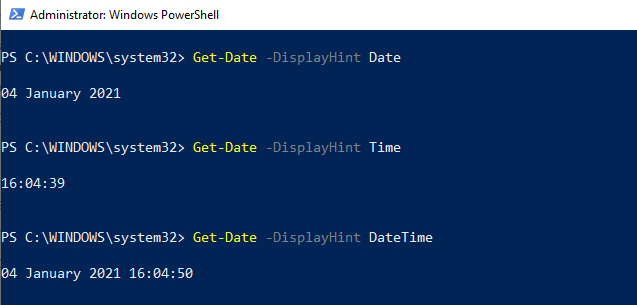 FormatUsing the -Format parameter in the PowerShell command, you can display date and time in a specific format that you specify. The -Format parameter accepts all values which are allowed in the Microsoft .Net framework and included in the DateTimeFormatInfo Class. There are different format options available that you can use to format your date and time results according to your requirement. Note that the result returned by -Format parameter is not the DateTime object; instead, they will a String result. We are mentioned some of the standard format specifiers information and their short description, which are provided by Microsoft.Standard Strings Format SpecifiersSome of the standard .NET strings format specifiers that are mostly used are defined below:
For example: Let see an example to retrieve the date and time in a .NET format specifier using the following - Format parameter and several .NET format specifiers: 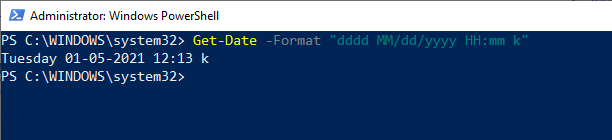 Optional Format list
Let's apply be following format one by one and see their output: 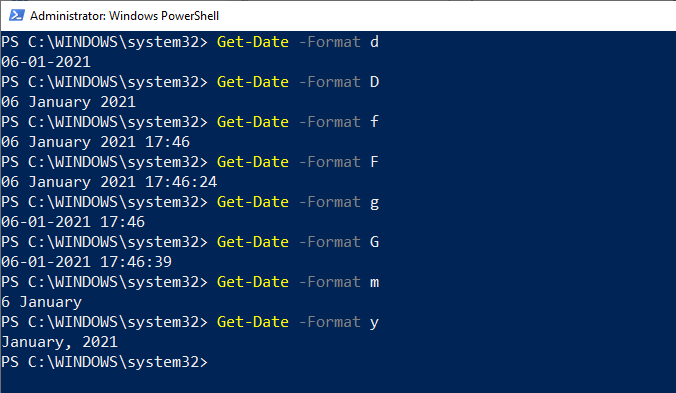 UFormatThe UFormat parameters allow us to mention a format that we want to display in Unix format. The syntax of this format command is as follows Get-Date -UFormat %\<value\>. The cmdlet -UFormat always returns an output as a String value. Below are various specifiers list and their descriptions that are used with -UFormat parameters provided by Microsoft. List of UFormat Specifiers
Get-Date with -UFormat parameter that uses various format specifiers returns a String output. For example, look at the result of the following -UFormat cmdlet:  How the above UFormat specifiers return the string value is defined below:
Calculate and display a date's day of the year (Get-Date -Year 2021 -Month 12 -Day 31).DayOfYear To calculate the date's of the year, the Get-Date uses three parameters to determine the date. These parameters are -Year, -Month, and -Day. Its command is enclosed within the parentheses so that the DayofYear property evaluates the output result. For example, calculating the total day at the given date of a year. 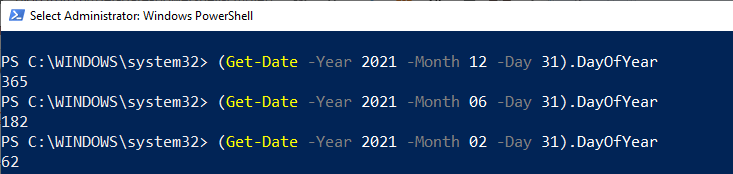 Checking whether a date is adjusted for daylight savings time: To check whether a date is adjusted for daylight savings time or not, it requires a boolean method. For example: 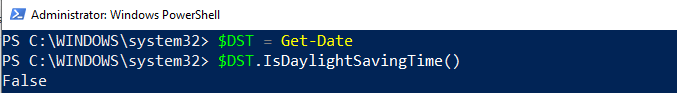 In the above command, we use a variable $DST that stores the result of Get-Date. A variable $DST calls the IsDaylightSavingTime() method to test whether a date is adjusted for daylight savings time or not. Convert the current time to UTC: The ToUniversalTime() method is used to convert the local system's current time into a Universal Time Coordinate (UTC). Let's see an example to convert current time to UTC offset. First of all, we will get the current date and time with UTC; after that, we convert it to Universal Time. 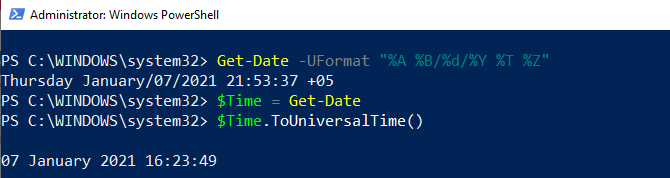 The Get-Date command uses a -UFormat parameter and some format specifiers to return the local system's current date and time. The format specifier %Z specifies the Universal Time Coordinate offset of +05. A variable $Time store the current date and time result returned by Get-Date. The returned value ($Time) calls the ToUniversalTime() method to convert the local system's current date and time to UTC offset. Create a timestamp using Get-Date -Format:To create a timestamp using the Get-Date -Format, let's see the following cmdlet example: 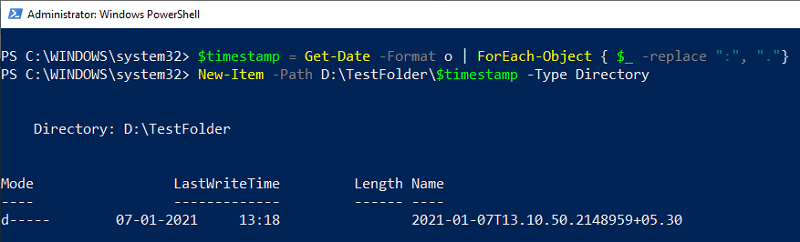 In the above example, the format specifier creates a timestamp String object for an input directory name. This timestamp contains values of date, time, and UTC offset. In the above command, a variable $timestamp stores the results of the Get-Date command. Get-Date uses the Format parameter and a format specifier o that creates a timestamp String object in lowercase. The object is sent back through the pipeline to ForEach-Object, and variable $_ represents the current pipeline object. The timestamp string values are specified by colons, which are replaced by periods. The New-Item uses a -Path parameter that determines the location for the newly-created directory. A variable $timestamp included in the path represents the directory name, and the -Time parameter indicates that a directory is created. 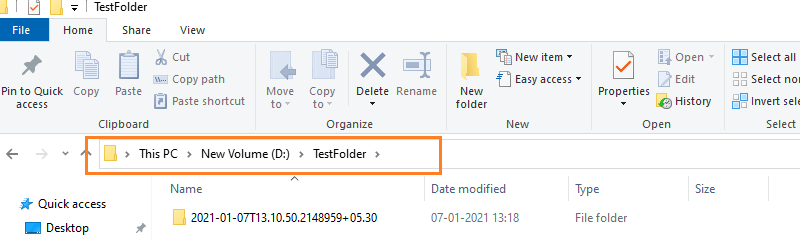 Next Topic# | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||