Profit DefinitionWhat is Profit?Profit is the amount of money a company or person keeps after deducting all costs and expenses from the income obtained from selling goods or services. It indicates the amount left over after paying all business expenses such as rent, electricity, and taxes. Most businesses' main goals are to make money, which is necessary for their existence and expansion. It is frequently stated in terms of a percentage of Revenue or a monetary value. You get profit for taking chances and giving customers something they value.  The Value of ProfitProfit is necessary for a business to be sustained and flourish over time. The following are some arguments in favor of profit: Business SurvivalA company must be profitable to survive. A company can only operate, meet its financial responsibilities, or engage in expansion if it makes a profit. InvestmentProfit is required for firms to invest in new machinery, technology, and product development. This aids in preserving a competitive edge and meeting shifting consumer needs. Employee WagesProfit is required to pay salaries, bonuses, and benefits to employees. This encourages workers to give their best efforts and aids in retaining top talent. Returns to ShareholdersEarning a profit is crucial for shareholders since they invest in a business hoping to get a return on their money. ExpansionProfit gives a company the resources it needs to grow, create new sites, or enter new markets. Profitability and Revenue may rise as a result. 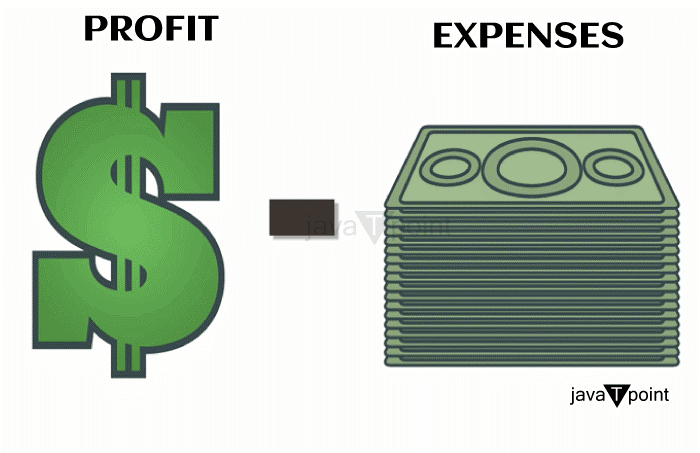 Profit is a general indicator of a business's performance and capacity to add value for its clients, staff, and shareholders. A business can only accomplish its objectives or carry out its mission by making a profit. Different Types of ProfitsThere are three primary categories of profit: Gross ProfitThe difference between Revenue and the cost of products sold is known as gross profit. (COGS). It indicates a business's Revenue from selling its goods or services before running costs like staff pay, rent, and marketing costs are subtracted. Operating ProfitAfter deducting all operating expenses, operating profit is a firm's profit from its primary business operations. It accounts for all costs of operating a firm, including rent, marketing, and depreciation. Net ProfitA firm's profit after deducting all costs, such as taxes and interest, is referred to as net profit, often known as the bottom line. It is the amount of money available for distribution to shareholders or reinvested back into the company, and it represents the actual profit a company makes. In conclusion, gross profit is the Revenue generated by a business's sales of goods or services, operational profit is the Revenue generated by its primary business activities, and net profit is the Revenue remaining after all costs have been paid. Each type of profit offers insightful data on the success and health of a company's finances. Comparing Gross and Net ProfitsGross and net profit are important measurements of a company's financial health, but they differ in what they represent and how they are computed. The difference between Revenue and the cost of products sold is known as gross profit. (COGS). It indicates the Revenue generated by a business's sales of goods or services before running costs like staff wages, rent, and marketing expenditures are subtracted. The below equation is used to compute gross profit: Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold In contrast, a company's net profit is its profit after deducting all costs, such as taxes and interest. It is the amount of money available for distribution to shareholders or reinvested back into the company, and it represents the actual profit a company makes. Calculating net profit is done as follows: Net Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold - Operating Expenses - Taxes - Interest All costs related to maintaining a firm, such as rent, marketing, and depreciation, are operating expenses. The primary distinction between gross profit and net profit is that. In contrast, net profit considers all operational costs, taxes, and interest, while gross profit accounts for the direct cost of producing goods or services. While net profit is a better measure of a company's total profitability, gross profit is a valuable metric to evaluate a company's pricing strategy and production efficiency.  In conclusion, whereas net profit shows the real profit made after deducting all costs, gross profit quantifies the profit made by selling goods or services. Both metrics are crucial to evaluate an organization's financial success and health. How to Determine Your ProfitAll costs must be subtracted from Revenue to determine profit. The profit calculation formula is as follows: Profit = Revenue - Expenses Here is a more thorough breakdown of how to determine profit: Calculate your IncomeThe total amount of money your company brings in through selling goods or services is known as Revenue. Determine your cost of goods sold (COGS)The direct cost of manufacturing your products or services is your COGS. The price of labor, raw materials, and production overhead are all included. Subtract COGS from RevenueThe gross profit is obtained by deducting the cost of goods sold. Deduct Operating ExpensesDeduct operating expenses include all costs related to maintaining a firm, such as rent, salaries, marketing, and depreciation. Calculate operating profit by deducting operating costs from gross profit. Deduct Taxes and InterestYour net profit is determined by deducting taxes and interest from your operating profit. Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold - Operating Expenses - Taxes - Interest It's crucial to frequently calculate profit to keep track of your company's finances, find areas where expenses can be cut, and assess how well your pricing and marketing tactics are working. Profitability Affecting FactorsSeveral variables can impact the profitability of a corporation. Among the most important ones are the following: Cost of Goods SoldOne important aspect that may impact profitability is COGS or the cost of goods sold. The profit margins will be smaller if the cost of manufacturing goods or services rises. Pricing PolicyA key element in determining profitability is pricing. Excessively high prices could prevent a business from losing clients to rivals. Conversely, if prices are set too low, they are not enough to cover costs and make a profit. CompetitionMarket competition can have an impact on a company's profitability. Maintaining market share may be difficult in a highly competitive environment, and pricing pressure may also impact profit margins. Economic CircumstancesA company's profitability may be affected by economic circumstances. Consumers may reduce their spending during a recession, affecting Revenue and profits. Operating EffectivenessA company's profitability may be impacted by operating effectiveness. Businesses that can efficiently create goods or services while lowering operational expenses might boost their profit margins. Interest RatesInterest rates can have an impact on the profitability of a business. A company's capacity to borrow money may cost more if interest rates rise, affecting its profitability. TaxesTaxes can affect a business's profitability. Profits can be decreased by higher taxes while being increased by lower taxes. In conclusion, the cost of goods sold, the pricing strategy, the level of competition, the state of the economy, the effectiveness of operations, interest rates, and taxation all impact profitability. Business owners can improve their financial health and sustain profitability by being aware of these aspects and regularly checking them. How to Boost ProfitProfit growth is a typical objective for many companies. Here are some strategies for boosting profits: Increase RevenueIncreasing Revenue is one of the most obvious strategies to boost profit. This can be accomplished by growing the clientele, boosting sales using efficient marketing techniques, and creating new goods or services. Concentrate on High-Profit Items or ServicesBy comparing the profitability of various goods or services, firms can concentrate on those that bring in the most money. This may entail eliminating or drastically lowering the production of goods or services with low-profit margins. Boost ProductivityBoosting productivity can save expenses and boost Revenue. This can be accomplished by enhancing manufacturing procedures, investing in new technology, and offering personnel training. Expand into New MarketsGrowing your business by entering new markets can boost your earnings. Finding new client segments, expanding into new geographical areas, or creating new goods or services can help. Cross-Selling and UpsellingTargeting current clients can boost sales and profit margins. This can be accomplished by finding complementary goods or services and promoting them to current clients. In conclusion, enhancing profit includes raising sales, cutting expenses, optimizing pricing, concentrating on high-profit goods or services, raising productivity, entering new markets, and cross- and up-selling. Finding the optimal tactics for each organization requires careful study and preparation. Profit MarginA financial indicator called profit margin calculates a company's profit as a proportion of its Revenue to determine its profitability. It displays the portion of income a business retains as profit after deducting all costs, including goods sold, operating costs, taxes, and interest. The profit margin is calculated using the following formula: (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100 = Profit Margin A company's net profit is its profit after deducting all costs. A business's total amount of money from selling goods or services is known as Revenue. Two primary categories of profit margin exist: Gross Profit MarginThe gross profit margin is the percentage of Revenue a company retains after subtracting the cost of goods. It displays the profitability of a business's primary activities. The gross profit margin is calculated using the formula: Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue x 100 Net Profit MarginA company's net profit margin is the portion of Revenue that remains after all costs, such as cost of goods sold, operating costs, taxes, and interest, have been subtracted. It displays a company's overall profitability. Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Revenue) x 100 is the formula for computing net profit margin Investors and analysts use profit margin as a key financial statistic to assess a company's financial health and how it stacks up against its rivals. Higher profit margins show that a business makes more money from its sales, which is generally regarded as a good indication. Profitability RatiosFinancial measurements, called profitability ratios, assess a company's capacity to profit from its operations. The following are a few frequently used profitability ratios: Gross Profit MarginThe gross profit margin, or proportion of Revenue, leaves over after deducting the cost of goods sold, giving the ratio. It is determined by: Gross Profit Margin = (Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue Net Profit MarginThe net profit margin, or proportion of income, leaves over after all costs, including taxes and interest, that have been subtracted. Net Profit Margin = Net Profit / Revenue 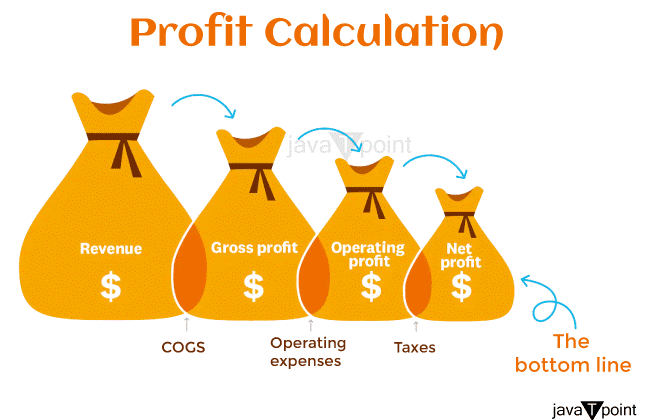 Return on AssetsReturn on Assets (ROA) is a ratio that assesses how effectively a business generates profit from its assets. It is determined by: ROA = Net Income / Total Assets Return on EquityReturn on Equity (ROE) is a ratio that expresses how much profit a business makes off each dollar shareholders invest. It is determined by: ROE = Net Income / Shareholder Equity Operating MarginThis ratio calculates the portion of Revenue left over after all operating costs have been paid. It is determined by: Operating Margin = Operating Income / Revenue EBITDA MarginThis ratio calculates the total Revenue left over after all operational costs, except depreciation and amortization, have been paid. It is determined by: EBITDA Margin = EBITDA / Revenue Profitability ratios assist analysts and investors in evaluating a company's capacity for profit and benchmarking it against its rivals. Higher ratios are generally regarded as good because they show that a company makes more money from its activities. Before making an investment decision, it is crucial to consider other aspects, such as the industry, the state of the economy, and the company's financial stability. Profit ManagementProfit management is a key element of a successful firm. Here are some pointers for-profit management that work: Create a BudgetA budget is a financial plan that details a business's anticipated Revenue and costs. Creating a budget can assist companies in managing their profits by giving them a framework for decision-making and highlighting areas where cost savings can be made. Keep Track of SpendingKeeping track of all business expenses is crucial for identifying areas where costs can be cut. Accounting software or other financial instruments can be used for this. Monitor Cash FlowA business's cash flow is the money it makes and spends on its activities. Profit management depends on efficient cash flow management. Making sure there is enough money on hand to pay bills and put money towards investment opportunities is crucial. Enhance Pricing StrategyIncreasing profit margins is another benefit of improving the pricing strategy. To do this, it is possible to analyze the market and the competitors, choose the ideal price point, and then change pricing as necessary. Cost- CuttingCost-cutting measures can boost business margins. This can be done through haggling with suppliers to lower the price of raw materials, increase operational effectiveness, and cut wasteful spending. Invest in TechnologyUsing technology effectively can help firms cut expenses, boost output, and enhance customer satisfaction. Utilizing automation tools, updating software and hardware, and incorporating cutting-edge innovations like artificial intelligence and machine learning are examples of how to do this. In conclusion, setting a budget, keeping track of spending, keeping an eye on cash flow, enhancing pricing strategy, cutting costs, and investing in technology are all necessary components of effective profit management. Finding the optimal tactics for each organization requires careful study and preparation. Next TopicProton Definition |