What is the full form of RDPRDP: Remote Desktop ProtocolRDP stands for Remote Desktop Protocol. Microsoft created the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), a proprietary protocol that enables remote access to Windows-based workstations. Users can view files, programmes, and other resources as if they were physically in front of the computer by connecting to a remote desktop. Businesses, educational institutions, and other organizations that need remote access to their systems frequently use RDP. The main advantages, features, and potential security issues of RDP will all be covered in this article.  The user needs a computer with RDP client software installed to use RDP. The RDP server software must be installed on the remote machine, which must also be running a version of Windows that supports RDP. Most Windows operating systems have this software by default, but third-party client software packages are also readily accessible for other platforms. History of RDPRDP is frequently used for remote technical help, remote administration, and telecommuting since it enables a user to remotely connect to and control a Windows desktop or server over a network connection. Microsoft first released RDP in 1998 as a component of its Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition. The protocol was created to enable several users with their unique desktop environment, apps, and data to access a single windows server concurrently. Later, RDP was incorporated into Windows versions such as Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows 10. Microsoft released RemoteFX in 2012 as a collection of RDP improvements that improve graphics performance and supports multimedia apps. Since Windows 8 and beyond, RemoteFX has been an integral feature of RDP. With improved security, remote printing, and the capacity to connect to remote computers over the internet, Microsoft has continued to develop and enhance RDP over time. With support from various independent software and hardware suppliers, RDP has become a widely used remote access and management protocol. However, RDP has been a target for security attacks just like any other technology that enables remote access. Therefore, it's crucial to ensure that RDP connections are properly secured and kept track of to avoid unauthorized access.  VersionsRDP has been introduced in several versions, each with improved features. The most recent major releases of RDP are listed below: RDP 1.0 In 1998, Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition included the first release of RDP. It included some basic remote access features but only a few sophisticated ones. RDP 5.0 RDP 5.0 was released alongside Windows 2000 Server and added several new features, including support for 24-bit colour, audio redirection, and improved printing capabilities. RDP 5.1 Released alongside Windows XP, this version of RDP included support for advanced functions like local resource redirection, smart card authentication, and support for multiple monitor setups. RDP 5.2 RDP 5.2 was released with Windows Server 2003 and added various new capabilities, such as IPv6 support, faster performance, and greater security. RDP 6.0 RDP 6.0 was released alongside Windows Vista, and it came with several new capabilities, including support for 32-bit colour, faster bitmap caching, and better performance over high-latency connections. 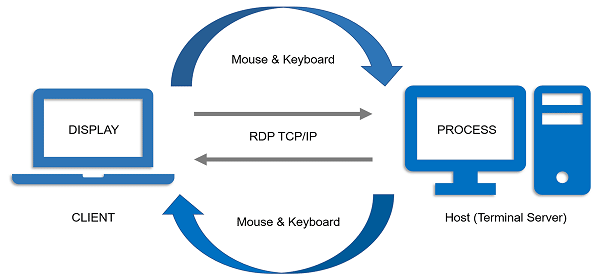 RDP 6.1 Windows Server 2008 came with this version of RDP, which added new capabilities like RemoteFX, which offers hardware acceleration for multimedia and graphics. RDP 7.0 Launched alongside Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, RDP 7.0 included several new capabilities, including enhanced WAN speed, support for bi-directional audio, and Windows Media Player redirection. RDP 8.0 This update to RDP, which came with Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, added new capabilities such as support for USB redirection and RemoteFX Adaptive Graphics, which improves graphics quality based on available bandwidth. RDP 8.1 RDP 8.1, released alongside Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, brought several new features, including support for network identification and automatic reconnection, improved touch functionality, and support for remote desktops with high DPI screens. RDP 10 Launched alongside Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016, RDP 10 has several new capabilities, including support for enhanced session mode, which offers greater security, and increased speed over slow connections. RDP Key FeaturesRDP's most important advantage is offering a safe and effective remote desktop experience. Here are a few of RDP's salient characteristics that make it a well-liked option for remote access: 1. Support for Multiple Operating Systems RDP is a multi-platform protocol that can run on Windows, macOS, Linux, and other platforms. This allows users to access their desktops from various gadgets, such as laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. RDP enables several users to connect to the same computer at once concurrently. This functionality is especially helpful when numerous people must work together on a project or access the same collection of documents and software. 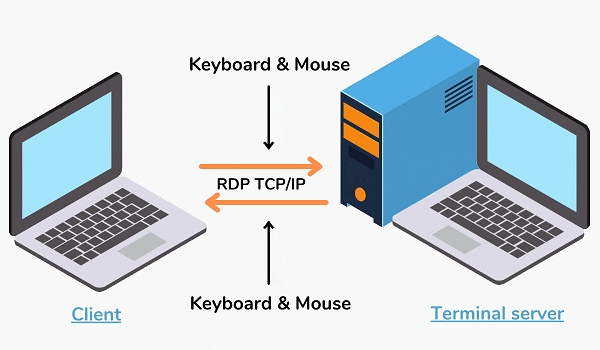 2. High-Quality Audio and Video Streaming RDP is capable of high-quality audio and video streaming, which is necessary for video conferencing and multimedia editing. Data transmission across the network is secure as RDP's uses 128-bit encryption and network-level authentication. As a result, only authorized users can access the remote desktop, preventing unwanted access. 3. Remote Control RDP enables users to interact virtually with Windows-based servers and desktops as if they were physically in front of the device. This makes it possible for system administration and assistance to be done remotely. 4. Remote Printing Remote printing is a feature of RDP that enables users to print files from a remote system to a local printer plugged into their computer. Attributes of RDPRDP's important attributes are the following:
RDP is built to allow multiple concurrent user sessions with their desktop environments, applications, and files on a single system. This enables shared access to systems for purposes of cooperation and assistance.
RDP is made to offer low-latency remote access, which means that user input and the resulting display updates must occur instantly with no discernible lag. Support for multimedia applications, including audio and video playing, is provided by RDP, enabling remote access to multimedia files like streaming music or video. Advantages of RDPBusinesses and organizations that need remote access to their systems can profit from RDP in several ways. The following are some of the main benefits of utilizing RDP: Enhanced Productivity RDP enables users to work whenever and from anywhere. As a result, productivity rises, and businesses can work more effectively. RDP reduces the need for expensive hardware and software changes, reducing IT costs. Businesses and organizations can save a lot of money by doing this. RDP enables administrators to control and manage any remote desktop connection from a single location. This lessens the strain on IT personnel and guarantees that all connections are safe and current. Enhanced Security RDP offers a safe remote access option which is perfect for companies and organizations that need to send sensitive data over the network. RDP uses encryption and authentication to protect data and ensure that only authorized users can access the remote desktop.  Remote Access With RDP, you can access a computer or server remotely from any location with an internet connection. This is especially helpful for companies with remote workers or IT specialists who must access servers from off-site locations. Several users can share the same resources on a single computer or server via RDP. Costs can be reduced, and productivity can rise as a result. Security RDP employs encryption to secure remote connections, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. Collaboration RDP enables people physically separated from one another to work together on the same project or task. This may contribute to greater productivity and efficiency. RDP offers a centralized management system that enables IT specialists to manage and set up remote access to several machines and servers from a single place. Simple to Use RDP is simple to use and accessible to people with varying levels of technical knowledge. RDP is an all-around strong and adaptable tool that enables users to operate from any location at any time. Businesses and organizations can utilize RDP to serve their remote access requirements safely and effectively by adhering to best practices and putting in place the necessary security safeguards. Disadvantages of RDPSecurity Risks If RDP is not configured correctly, it may be subject to security hazards. Unauthorized users who obtain access to an RDP session may be able to view confidential information, spread malware, or harm the system. Prerequisites for Bandwidth RDP needs a fast internet connection to work correctly, which might be difficult in rural or low-bandwidth places. Poor performance, lag, and even disconnections may result from this. RDP is a Microsoft protocol. Hence it can only be used with Windows-based systems. Users cannot connect to non-Windows systems like Mac or Linux via RDP. System Compatibility RDP may not work with all computer setups and operating systems, limiting certain users ability to use it effectively. RDP licencing fees per user could be an issue for companies with many users because of the potential cost. Limits of Remote Control Although RDP offers remote access to a desktop or server, there may be certain restrictions on what can be done there, such as accessing particular hardware or executing particular programmes. RDP Security ConcernsWhile RDP has many advantages, using it could raise certain security issues. The following are some of the main security risks connected to RDP:
RDP is susceptible to brute force assaults, in which criminals use automated tools to try and guess user names and passwords. Implementing account lockout procedures and strong passwords is crucial to reducing this risk.
Malware can use RDP to access a system. Updating antivirus software and software is essential, and only authorized users should be allowed access to RDP to reduce this danger. RDP is susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks, in which criminals intercept and change data transmitted across the network. Utilizing encryption and authentication procedures and avoiding public Wi-Fi networks will help reduce this danger. RDP is susceptible to denial-of-service assaults, where attackers saturate the network with traffic and crash the machine. It's crucial to utilize firewalls and intrusion detection systems to find and stop such assaults reducing this danger. RDP combines TCP and UDP protocols to send data over the network. RDP can adapt itself automatically to the available bandwidth and supports a wide range of network speeds. RDP utilizes port 3389 by default, although this can be adjusted if necessary. RDP can provide some security hazards. Thus, it's crucial to utilize it safely and to be aware of those dangers before using it. Patents of Remote Desktop ProtocolThe specifics of these patents are not typically made public, though, as they are regarded as proprietary, sensitive information. It's important to point out that Microsoft has a Remote Desktop Protocol Licensing Program that enables outside businesses to obtain licences for the usage of RDP for their goods and services. This software comes with various licencing options, such as a client access licence (CAL) that enables a third-party product to connect to a Windows server running RDP and a technology licence that enables a third-party business to include RDP functionality in their goods or services. Companies who use RDP in their goods or services must ensure they have the appropriate licences and comply with Microsoft's licencing guidelines. Patent and licence agreement violations may result in legal action, financial penalties, and reputational damage for the offending business. Use of Remote Desktop Protocol in CybercrimeA popular remote access and management solution for Windows-based computers are Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). Regrettably, fraudsters routinely use RDP to their advantage, stealing sensitive information, spreading malware, and obtaining illegal access to networks. Cybercriminals frequently search the internet for computers with open RDP ports before attempting to brute-force or guess user names and passwords to obtain access. Once they access a system, they may exploit it for various harmful purposes, including data theft, launching more assaults on other systems, and distributing ransomware or other forms of malware. Another strategy hackers employ is exploiting flaws in RDP or other RDP software, such as virtual private networks (VPN) or remote access tools. Exploiting these flaws can provide attackers access to systems without authorization or the ability to run arbitrary code, which can be used to steal data, install malware, or do other kinds of harm. It is crucial to adhere to best practices for safeguarding remote access, such as using strong passwords or multi-factor authentication, limiting access to only authorized people and devices, and routinely monitoring RDP connections for the nefarious activity to reduce the risks connected with RDP. Additionally, it's crucial to frequently check access logs for indications of illegal access or unusual activity and maintain RDP and related software up-to-date with the most recent security patches. Non-Microsoft RDPSome Non-Microsoft RDP implementations can offer remote access to desktops or servers, even though Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a Microsoft protocol integrated into the Windows operating system. Some Non-Microsoft RDP implementations are shown here: Free-RDP Free-RDP is an open-source RDP implementation that enables non-Windows operating systems like Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD to connect to Windows servers or desktops. In addition to supporting advanced features like network-level authentication (NLA) and RemoteFX, it is compatible with Microsoft's RDP protocol. XRDP Running on Linux, XRDP is an open-source RDP implementation that enables remote access to Linux servers or desktops from Windows or other platforms. It offers sound, printer redirection, and clipboard-sharing support and is compatible with Microsoft's RDP protocol. Apache Guacamole Using the RDP, VNC, SSH, and Telnet protocols, Apache Guacamole is an open-source web application that offers remote desktop access. It enables users to connect to Windows desktops or servers from any platform that supports a web browser and access remote desktops from a web browser without installing any additional software. Thinfinity Remote Desktop Commercial RDP server Thinfinity Remote Desktop Server enables safe remote access to Windows desktops or servers from any device equipped with an HTML5 web browser. It can be used and has capabilities like remote printing, file transfer, and session recording. It can be utilized in various areas, including healthcare, education, and finance, and contains capabilities like session recording, file transfer, and remote printing. In general, these non-Microsoft RDP implementations provide several options for remote desktop access. They may be helpful for users who don't use the Windows operating system. Next TopicFull Forms List |