Recursive Descent ParserA top-down parser is known as a recursive descent parser that analyses input based on grammar rules using recursive methods. Starting with the grammar's topmost rule, the parser executes subroutines backward for each input symbol that is not a terminal symbol until it reaches one. A parse tree representing the input's structure according to the grammar is the parser's output. Recursive Parser Descent:The process of parsing is frequently employed in language processing and compiler design. It is founded on the idea that a difficult problem can be broken down into simpler problems and then solved recursively. Starting with a top-level nonterminal symbol, the parsing process proceeds by recursively expanding nonterminals until it reaches terminal symbols. Repeated descent, the fundamental idea behind parsing is to create a set of parsing functions, each of which corresponds to a nonterminal grammar symbol. These procedures are responsible for locating and assessing the relevant linguistic components. The top-level function is called first by the parser, which then calls the necessary parsing routines recursively depending on the structure of the input. 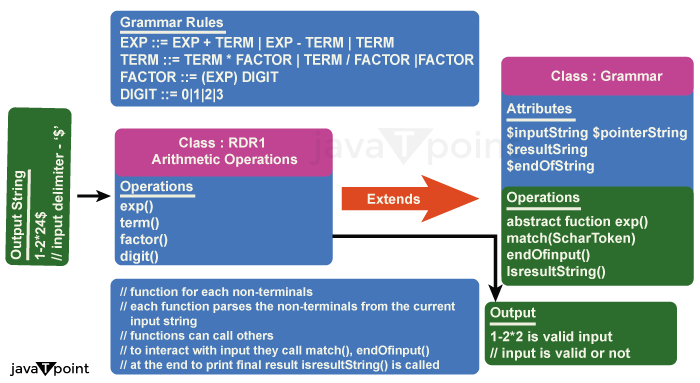 Grammar:Defining the grammar of the language to be parsed is the first stage in developing a recursive descent parser. A collection of rules known as grammar define the syntax of a language. Each rule is made up of a series of terminal and nonterminal symbols on the right side and a nonterminal symbol on the left side. Take the grammar for a straightforward arithmetic language, for instance: Expression, term, factor, and number are the grammar's four nonterminal symbols. An arithmetic expression is defined as one or more terms divided by plus or minus signs by the expression rule, which serves as the foundation for parsing. According to the term rule, a term is defined as one or more factors divided by multiplication or division signs. A number or an expression surrounded in brackets is what the factor rule refers to as a factor. As per the number rule, a number consists of one or more digits. Parsing:The fundamental principle of recursive descent is Writing a collection of recursive functions, one for each nonterminal symbol in the grammar, is the process of parsing. A series of symbols that matches a particular rule must be parsed by each function, which is assigned to a grammar rule. The expression function, which is invoked with the input string, is where the recursive descent parser begins. Depending on whether the symbol is a number or an opening parenthesis, the function analyses the first symbol of the input and chooses which alternative of the term rule to apply. The factor function is used to parse the symbol's value if it is a number. The expression function is used recursively to parse the expression inside the parentheses if the symbol is an opening parenthesis. The term function is invoked recursively to parse any subsequent multiplication or division signs and factors after the factor or expression function has returned. The expression function determines whether there are any plus or minus signs after the term if the term function returns a value. If so, the term function is invoked once more to parse the subsequent term. Until an error happens or all of the input has been parsed, this procedure continues. Say, for instance, that we want to parse the formula 2 + 3 * (4 - 1) / 2. This is how the recursive descent parser operates: The parser first calls the expression function with the supplied string. When "2" is provided as input, the function calls another function, which then executes the data and returns. The expression function then reads the next symbol, a plus sign. It again calls the term function with the input ",". Recursive descent parsing has the following benefits:
Recursive descent parsing, however, also has certain drawbacks:
An outline of the Recursive Descent Parsing algorithm is provided below:
The Recursive Descent Parsing algorithm can be used to parse a given language by its grammatical rules by carrying out the stages listed below. Implementation of Code:Output: 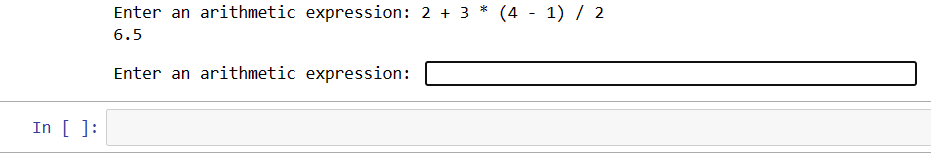 The given code implements a simple calculator application that evaluates arithmetic expressions.
Conclusion:Recursive descent parsing is a key method in compiler design and parsing theory overall. It is a popular option for simple languages and educational reasons since it offers a simple and intuitive way of parsing. Anyone interested in language parsing and compiler development would benefit from understanding the fundamentals and practical use of recursive descent parsers. Next Topic# |