SAS FunctionsIn this topic, we are going to discuss the SAS functions. Functions allow us to do extensive manipulation in data and existing data sets of SAS. SAS provides a wide variety of built-in functions that are used in data processing and analysis. We use these functions as a part of the DATA statements. A function accepts variables as arguments and provides a result, and this result can be stored into another variable. The number of arguments can vary, on the basis of the type of the function. Some functions accept a fixed number of arguments while some accept zero arguments Syntax:To implement a function, use the following syntax: Where, FUNCTIONNAME: It is the name of the SAS built-in function. Argument: It is the value provided to the function so that it can take instructional action. The argument can be a variable, constant expression, or another function. Depending on the data type, functions are categorized in the following categories:
Character FunctionsCharacter functions are used to manipulate character or string values. Following are the various SAS built-in character functions used to manipulate string values:
Example:Execute the above code in SAS Studio: 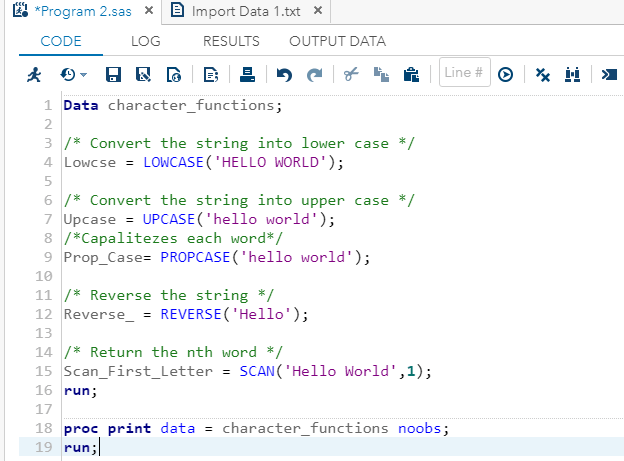 Output: 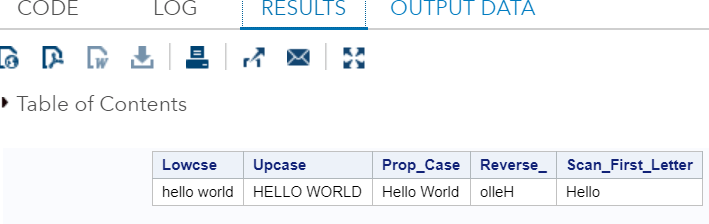 Date and Time FunctionsDate and time functions are used to process date and time values. Following are the various SAS built-in Date and Time functions used to manipulate date and time values:
Example:Execute the above code in SAS Studio: 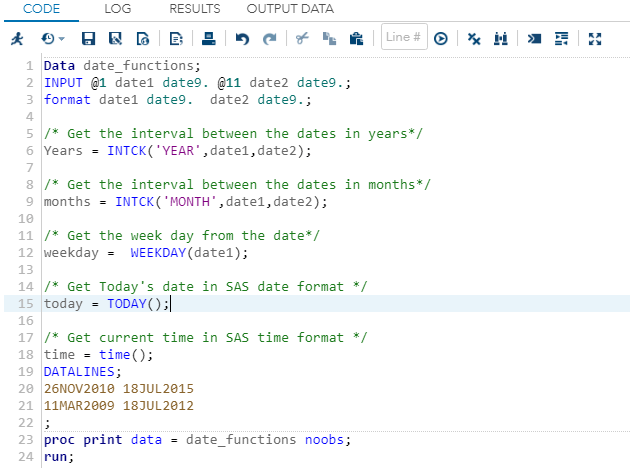 Output: 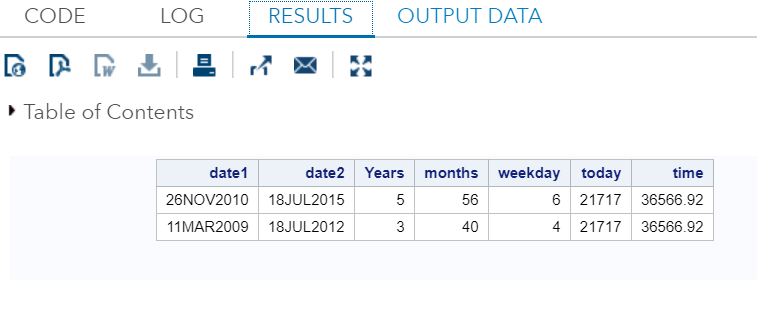 Mathematical Functions:Mathematical Functions are used to apply mathematical calculations on the numeric or variable values. Following are the SAS built-in Mathematical Functions used to perform calculations on numeric values:
Example:Execute the above code in SAS Studio: 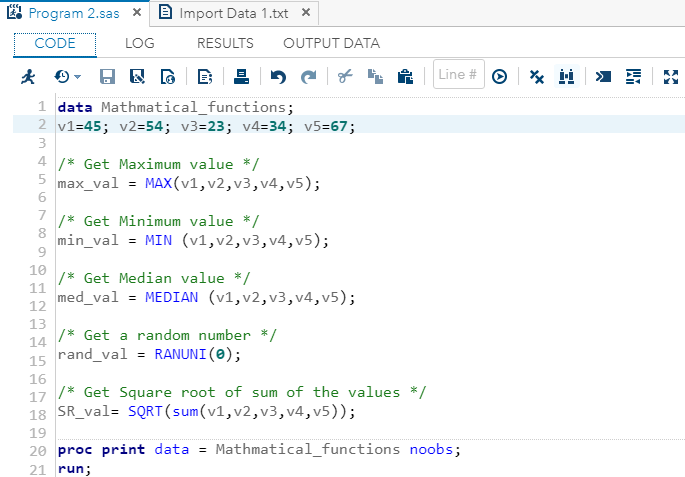 Output: 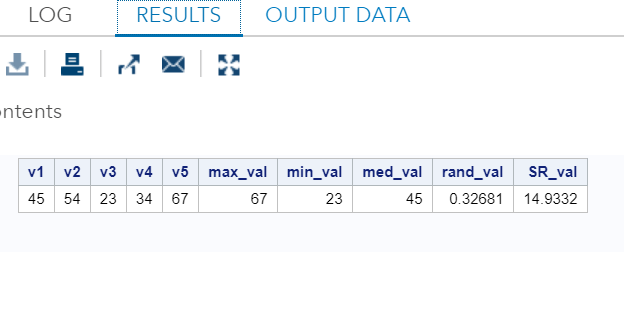 Truncation FunctionsTruncation Functions are used to truncate numeric values. Following are the SAS built-in Truncation functions used to perform truncation on the integer values.
Example:Execute the above code in SAS Studio: 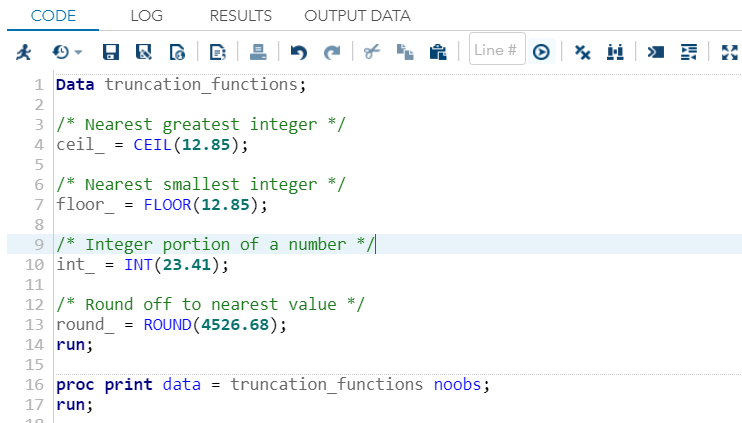 Output: 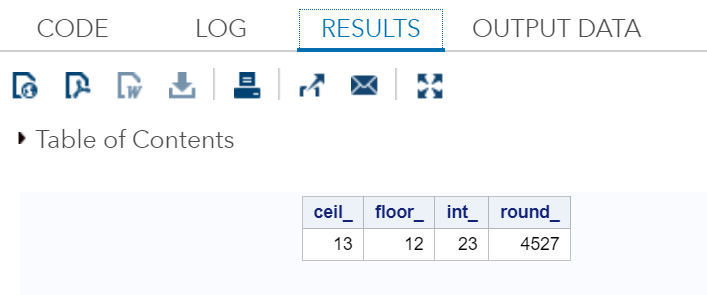 Miscellaneous FunctionsLet's now understand two miscellaneous functions of SAS which are usually used.
ZIPSTATEIt returns the upper-case two-letter state postal code (or global GSA geographic code for U.S. territories) that corresponds to its five-digit ZIP state code. Example: Here we are taking zipstate code 27511 which corresponds to global GSA geographic code NC for U.S. territories. Execute the above code in SAS Studio: 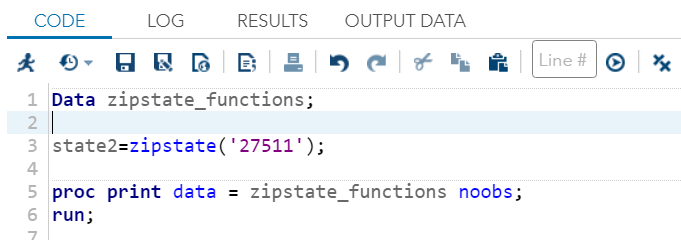 Output: 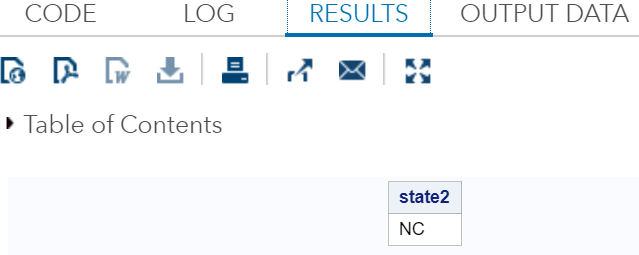 MortIt returns amortization parameters. Syntax: Where, a: It is a numeric value which specifies the initial amount. p: It is a numeric value which specifies the periodic payment. r: It is a numeric value which specifies the periodic interest rate, which is expressed as a fraction. n: It is an integer value which specifies the number of compounding periods. Example: The amount of ₹ 50,000 is borrowed for 30 years at an annual interest rate of 10 percent. It compounded monthly. So, the monthly payments can be expressed as follows: Execute the above code in SAS Studio: 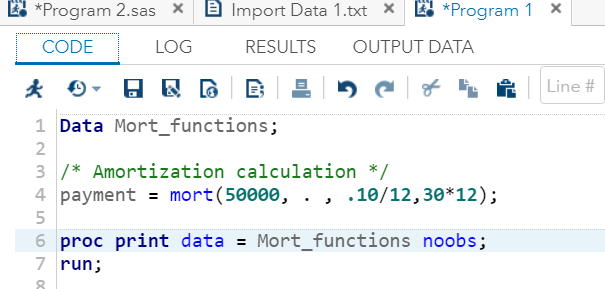 Output: 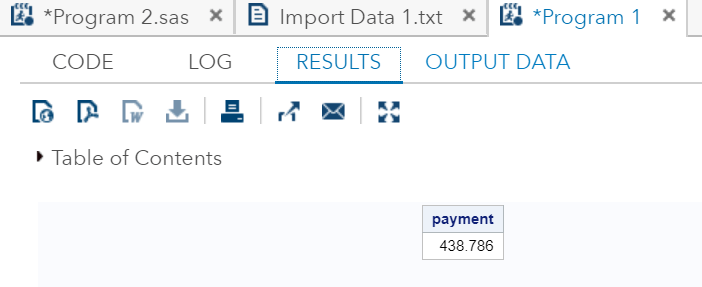 Next TopicSAS Macro |