Stress Definition in PsychologyAny change that strains the body, mind, or emotions is called stress. Stress is the body's response to anything that requires attention or activity. Stress affects everyone to some degree. However, how you respond to stress significantly influences how you feel generally. It can be essential to change your situation to manage your stress adequately. Changing your response to the situation is occasionally the best course of action. Definition of Stress Stress is our reaction while under pressure or when we feel endangered. It often occurs when we are put in a circumstance that we don't feel controlled or can handle. When we are under stress, things like
Stress Types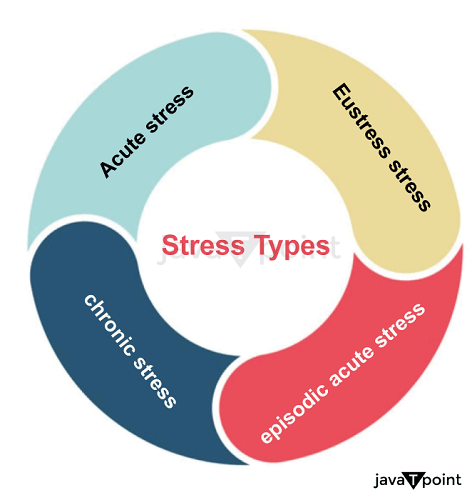 Stress cannot always have adverse effects or even be dangerous. Acute, chronic, and episodic acute stress are the three primary unfavorable types of stress. While chronic stress lasts long, acute stress is often short-lived yet occurs frequently. Eustress, sometimes known as enjoyable stress, can be demanding but can also have adverse effects. There are several stresses that you could experience, such as the following
Causes of Stress A wide variety of various situations in life may bring on stress. Work, economics, relationships, children, and everyday difficulties are a few of the significant stresses. The fight-or-flight reaction, which the body uses when it perceives a threat or danger, can be created by stress. The body produces hormones like cortisol and adrenaline during a stress response. It can boost energy and strength by increasing the heart rate, slowing digestion, redirecting blood flow to the larger muscle groups, and changing the activity of the autonomic nerves. The fight-or-flight reaction was initially meant to defend ourselves or flee from danger physically. Still, it can be triggered today when those actions are unnecessary, like during rush hour traffic or a busy workday. The relaxation reaction helps systems return to regular operation when a perceived threat has passed. Being in a constant fight-or-flight state can harm the body, but chronic stress situations often don't allow the relaxation reaction to occur frequently enough. Also, stress might cause destructive behaviors that are detrimental to your health. Many people, for instance, deal with stress by overeating or smoking. Over time, these destructive behaviors harm the body, leading to more severe issues. Influence of Stress Stress may have a substantial adverse influence on your health and well-being. It can make it harder to handle the challenges of everyday life, which may harm your relationships and overall health. It's crucial to comprehend how stress impacts both your mind and body. Relationship issues, financial problems, and living situations can cause stress, negatively affecting physical health. Stress levels and self-confidence can both be impacted by health conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. Your body responds due to your brain being under a lot of stress. Arrhythmias, Heart attacks, and even sudden death can result from extremely high levels of acute stress, such as those brought on by experiencing a natural catastrophe or verbal disagreement. Most people who already have heart disease still deal with this. Stress can also have an adverse emotional impact. A prolonged state of stress can also cause depression, anxiety disorders, and burnout, in addition to the milder worry or discomfort that might result from various forms of stress. Ongoing stress can harm your health. Consistent stress can cause your autonomic nervous system to become overly active, potentially harming your health. How stress may affect you You could feel the following when under stress
Symptoms of Stress on the Body The hormones our bodies release in reaction to stressful experiences may have various physical effects. These results might consist of the following
How Stress Affects How You Act When you're under pressure, you might
Stress Treatment Stress is not a condition that has a specific treatment. However, certain stress-related symptoms and indicators can be treated. They could be helpful if you are having trouble handling your stress alone. 1. Consulting Your Doctor
Your doctor may order specific tests to determine whether stress is responsible for your physical health issues and how to treat the symptoms. They could provide advice on relaxation and well-being to help you handle your stress. If social prescribing is offered in your region, they can recommend you to it. A community-based treatment called social prescribing assists you in addressing social problems that impact your health. For instance, this may involve assistance with physical exercise, financial difficulties, or loneliness. Additionally, it can assist you in locating chances for volunteering or pursuits that enhance your wellness, including painting and gardening lessons. 2. MedicationThere is no particular medicine that can relieve stress. However, some of the symptoms and indicators of stress can be lessened or managed with medication.
Alternative and Complementary TherapiesSeveral complementary and alternative therapies might be beneficial for treating stress-related symptoms and indicators. It could contain
Next TopicAlkali Definition |