Structure of Java ProgramJava is an object-oriented programming, platform-independent, and secure programming language that makes it popular. Using the Java programming language, we can develop a wide variety of applications. So, before diving in depth, it is necessary to understand the basic structure of Java program in detail. In this section, we have discussed the basic structure of a Java program. At the end of this section, you will able to develop the Hello world Java program, easily. 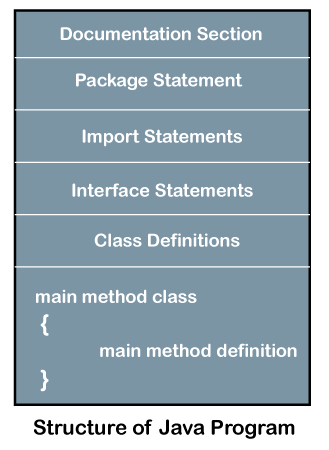
Let's see which elements are included in the structure of a Java program. A typical structure of a Java program contains the following elements:
Documentation SectionThe documentation section is an important section but optional for a Java program. It includes basic information about a Java program. The information includes the author's name, date of creation, version, program name, company name, and description of the program. It improves the readability of the program. Whatever we write in the documentation section, the Java compiler ignores the statements during the execution of the program. To write the statements in the documentation section, we use comments. The comments may be single-line, multi-line, and documentation comments.
Package DeclarationThe package declaration is optional. It is placed just after the documentation section. In this section, we declare the package name in which the class is placed. Note that there can be only one package statement in a Java program. It must be defined before any class and interface declaration. It is necessary because a Java class can be placed in different packages and directories based on the module they are used. For all these classes package belongs to a single parent directory. We use the keyword package to declare the package name. For example: Import StatementsThe package contains the many predefined classes and interfaces. If we want to use any class of a particular package, we need to import that class. The import statement represents the class stored in the other package. We use the import keyword to import the class. It is written before the class declaration and after the package statement. We use the import statement in two ways, either import a specific class or import all classes of a particular package. In a Java program, we can use multiple import statements. For example: Interface SectionIt is an optional section. We can create an interface in this section if required. We use the interface keyword to create an interface. An interface is a slightly different from the class. It contains only constants and method declarations. Another difference is that it cannot be instantiated. We can use interface in classes by using the implements keyword. An interface can also be used with other interfaces by using the extends keyword. For example: Class DefinitionIn this section, we define the class. It is vital part of a Java program. Without the class, we cannot create any Java program. A Java program may conation more than one class definition. We use the class keyword to define the class. The class is a blueprint of a Java program. It contains information about user-defined methods, variables, and constants. Every Java program has at least one class that contains the main() method. For example: Class Variables and ConstantsIn this section, we define variables and constants that are to be used later in the program. In a Java program, the variables and constants are defined just after the class definition. The variables and constants store values of the parameters. It is used during the execution of the program. We can also decide and define the scope of variables by using the modifiers. It defines the life of the variables. For example: Main Method ClassIn this section, we define the main() method. It is essential for all Java programs. Because the execution of all Java programs starts from the main() method. In other words, it is an entry point of the class. It must be inside the class. Inside the main method, we create objects and call the methods. We use the following statement to define the main() method: For example: You can read more about the Java main() method here. Methods and behaviorIn this section, we define the functionality of the program by using the methods. The methods are the set of instructions that we want to perform. These instructions execute at runtime and perform the specified task. For example: When we follow and use the above elements in a Java program, the program looks like the following. CheckPalindromeNumber.java Output: 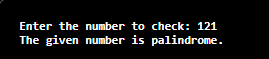
Next TopicWhy We Use Constructor in Java
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










