What is Mobile IP?Mobile IP or MIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) RFC 2002, De-Facto standard communication protocol. It is created by extending Internet Protocol, IP. The Mobile IP allows mobile device users to move from one network to another while maintaining the same permanent IP address. The concept and role of Mobile IP are very important in the field of mobile computing technology. The mobile IP makes the communication flawless and ensures that the communication will occur without the user's sessions or connections being dropped. Mobile IP is based on IP, so it is scalable for the Internet. Any media that supports IP can also support Mobile IP. Introduction to Mobile IP TechnologyIn IP networks, when a device is within its home network, the routing is based on the static IP addresses. The device within a network is connected through normal IP routing by the IP address assigned on the network. It is the same as how a postal letter is delivered to the fixed address on the envelope. The problem occurs when a device goes away from its home network and is no longer reachable using normal IP routing. In this condition, the active sessions of the device are terminated. The idea of Mobile IP was introduced to resolve this issue. It facilitates users to keep the same IP address while going to a different network or a different wireless operator without being communication disrupted or without sessions or connections being dropped. The mobility function of the Mobile IP is performed on the network layer rather than the physical layer. The architecture of Mobile IP TechnologyThe components of the Mobile IP and the relationship among them are specified in the following image: 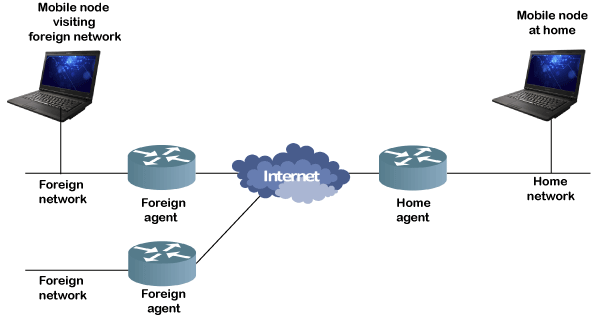 This is the architecture of Mobile IP technology. It consists of the following components:
Mobile Node The Mobile Node is a device or a user or a router that can frequently change their network positions without changing its original IP address. Examples of mobile nodes are cell phone, personal digital assistant (PDA), laptop, etc. whose software enables network roaming capabilities. Home Agent The Home Agent is a router on the home network. It serves as the anchor point for communication with the Mobile Node. Foreign Agent The Foreign Agent is a router that provides several services such as tunneling data-grams whenever a mobile node visits a foreign network. It is responsible for delivering packets from the Home Agent to the Mobile Node. Home Network The home network is the base station network to which the mobile node originally belongs to. Foreign Network Any network other than the home network or the networks on which mobile nodes have a registered IP is called a foreign network. Corresponding Node The partner nodes which are used for communication with mobile nodes are called corresponding nodes. Care of Address The Care of Address or COA is used to define the mobile node's current position or user. It is used to deliver data packets through the process of tunneling. Working of Mobile IPThe working of Mobile IP can be described in 3 phases: Agent Discovery In the Agent Discovery phase, the mobile nodes discover their Foreign and Home Agents. The Home Agent and Foreign Agent advertise their services on the network using the ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP). Registration The registration phase is responsible for informing the current location of the home agent and foreign agent for the correct forwarding of packets. Tunneling This phase is used to establish a virtual connection as a pipe for moving the data packets between a tunnel entry and a tunnel endpoint. Applications of Mobile IPThe mobile IP technology is used in many applications where the sudden changes in network connectivity and IP address can cause problems. It was designed to support seamless and continuous Internet connectivity. It is used in many wired and wireless environments where users have to carry their mobile devices across multiple LAN subnets. Although Mobile IP is not required within cellular systems such as 3G, it is often used in 3G systems to provide seamless IP mobility between different packet data serving node (PDSN) domains. |