Most Asked Apache Spark Interview Questions1) What is Apache Spark?Apache Spark is an open-source, easy to use, flexible, big data framework or unified analytics engine used for large-scale data processing. It is a cluster computing framework for real-time processing. Apache Spark can be set upon Hadoop, standalone, or in the cloud and capable of assessing diverse data sources, including HDFS, Cassandra, and others. Apache Spark provides an interface for entire programming clusters with implicit data parallelism and fault tolerance. Apache Spark is one of the most successful projects in the Apache Software Foundation. It is evolved as the market leader for Big Data processing. Nowadays, many organizations run Spark on clusters with thousands of nodes. Some big companies which have adopted Apache Spark are Amazon, eBay, Yahoo etc. 2) What type of big data problems Apache Spark can solve?As we know that Apache Spark is an open-source big data framework. It provides an expressive APIs to facilitate big data professionals to execute streaming and batching efficiently. It is designed for fast computation and also provides a faster and more general data processing platform engine. Apache Spark was developed at UC Berkeley in 2009 as an Apache project called "lighting fast cluster computing". It can distribute data in a file system across the cluster and processes that data in parallel. Using Spark, we can write an application in Java, Python, Scala or R language. 3) What was the need for Apache Spark?Many general-purpose cluster computing tools in the market, such as Hadoop MapReduce, Apache Storm, Apache Impala, Apache Giraph and many more. But each one has some limitations in its functionalities. We can see the limitations as:
Here, we can see that no single engine can perform all the tasks together. So, there was a requirement of a powerful engine that can process the data in real-time (streaming) and batch mode and respond to sub-second and perform in-memory processing. This is how Apache Spark comes into existence. It is a powerful open-source engine that offers interactive processing, real-time stream processing, graph processing, in-memory processing and batch processing. It provides a very fast speed, ease of use, and a standard interface simultaneously. 4) Which limitations of MapReduce Apache Spark can remove?Apache Spark was developed to overcome the limitations of the MapReduce cluster computing paradigm. Apache Spark saves things in memory, whereas MapReduce keeps shuffling things in and out of disk. Following is a list of few things which are better in Apache Spark:
5) Which languages Apache Spark supports? / Which are the languages supported by Apache Spark?Apache Spark is written in Scala language. It provides an API in Scala, Python, Java, and R languages to interact with Spark. 6) What is the key difference between Apache Spark and MapReduce?Following is the list of main differences between Apache Spark and MapReduce:
7) What are the most important categories of the Apache Spark that comprise its ecosystem?Following are the three important categories in Apache Spark that comprise its ecosystem:
8) What is the difference between Apache Spark and Hadoop?The key differences between Apache Spark and Hadoop are specified below:
Let's compare Hadoop and Spark-based on the following aspects:
9) What are some key features of Apache Spark?Following is the list of some key features of Apache Spark: Polyglot: Spark provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R. We can write Spark code in any of these four languages. It provides a shell in Scala and Python. The Scala shell can be accessed through ./bin/spark-shell and Python shell through ./bin/pyspark from the installed directory. Speed: Apache Spark provides an amazing speed upto 100 times faster than Hadoop MapReduce for large-scale data processing. We get this speed in Spark through controlled partitioning. Multiple Formats: Apache Spark supports multiple data sources like Parquet, JSON, Hive and Cassandra. These data sources can be more than just simple pipes that convert data, pull it into Spark, and provide a pluggable mechanism to access structured data though Spark SQL. Evaluation is lazy: Apache Spark doesn't evaluate itself until it is necessary. That's why it attains an amazing speed. Spark adds them to a DAG of computation for transformations, and they are executed only when the driver requests some data. Real-Time Computation: The computation in Apache Spark is done in real-time and has less latency because of its in-memory computation. Spark provides massive scalability, and the Spark team has documented users of the system running production clusters with thousands of nodes and supports several computational models. Hadoop Integration: Apache Spark is smoothly compatible with Hadoop. This is great for all the Big Data engineers who work with Hadoop. Spark is a potential replacement for the MapReduce functions of Hadoop, while Spark can run on top of an existing Hadoop cluster using YARN for resource scheduling. Machine Learning: The MLlib of Apache Spark is used as a component of machine learning, which is very useful for big data processing. Using this, you don't need to use multiple tools, one for processing and one for machine learning. Apache Spark is great for data engineers and data scientists because it is a powerful, unified engine that is both fast and easy to use. 10) What are the different cluster managers available in Apache Spark?There are mainly four types of cluster managers available in Apache Spark: Standalone Mode: The Apache Spark Standalone Mode cluster is a by default cluster where submitted applications will run in FIFO order. Each application will try to use all available nodes. You can launch a standalone cluster manually by starting a master and workers by hand or using our provided launch scripts. It is also possible to run these daemons on a single machine for testing. Apache Mesos: Apache Mesos is an open-source project to manage computer clusters and run Hadoop applications. The advantages of deploying Spark with Mesos include dynamic partitioning between Spark and other frameworks and scalable partitioning between multiple instances of Spark. Hadoop YARN: Apache YARN is the cluster resource manager of Hadoop 2. We can run Spark on YARN as well. Kubernetes: Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. 11) What is the benefit of learning MapReduce if Spark is better than MapReduce?Apache Spark is indeed better than MapReduce, but we should learn MapReduce first because MapReduce is a paradigm that is used by many big data tools, including Spark as well. When the data grows extremely bigger, then it is great to use MapReduce. Most tools like Pig and Hive convert their queries into MapReduce phases to optimize them better. 12) What do you understand by the term Sparse Vector in Spark?In Apache Spark, the sparse vector is a vector that has two parallel arrays, one for indices, and one for values. This is used for storing non-zero entities to save space. 13) Explain the architecture of Apache Spark and how it runs applications?The Apache Spark applications run as independent processes coordinated by the SparkSession object in the driver program. 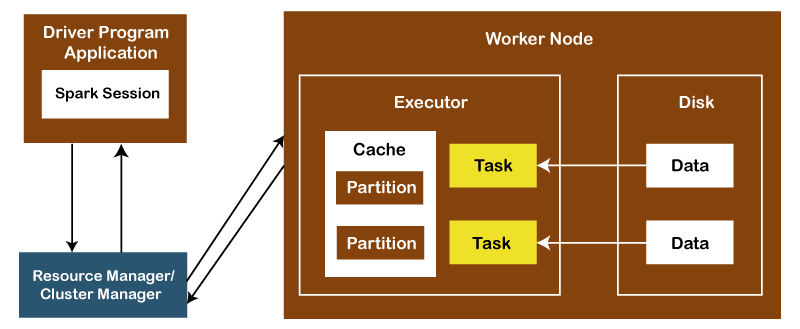
First, the resource manager or cluster manager assigns tasks to the worker nodes with one task per partition. Iterative algorithms then apply operations repeatedly to the data so they can benefit from caching datasets across iterations. A task applies its unit of work to the dataset in its partition and outputs a new partition dataset. Finally, the results are sent back to the driver application or can be saved to the disk. 14) What is RDD in Spark?RDD in Apache Spark stands for Resilient Distributed Datasets. It is a fundamental data structure of Spark that acts as an immutable distributed collection of objects. Each dataset in RDD is divided into logical partitions, which are computed on different cluster nodes. RDDs can contain any Python, Java, or Scala objects, including user-defined classes. 15) What is Dstream in Apache Spark?Dstream stands for Discretized Stream. It is a sequence of Resilient Distributed Database (RDD) representing a continuous stream of data. There are several ways to create Dstream from various sources like HDFS, Apache Flume, Apache Kafka, etc. 16) What do you understand by YARN?Just like in Hadoop, YARN is one of the key features in Apache Spark, which is used to provide a central and resource management platform to deliver scalable operations across the cluster. Spark can run on YARN, as the same way Hadoop Map Reduce can run on YARN. 17) Is it necessary to install Spark on all nodes of the YARN cluster?No. It doesn't seem necessary to install Spark on all YARN cluster nodes because Spark runs on top of the YARN. Apache Spark runs independently from its installation. Spark provides some options to use YARN when dispatching jobs to the cluster, rather than its built-in manager or Mesos. Besides this, there are also some configurations to run YARN, such as master, deploy-mode, driver-memory, executor-memory, executor-cores, and queue. 18) What are the different data sources available in SparkSQL?There are the following three data sources available in SparkSQL:
19) Which are some important internal daemons used in Apache Spark?Following are the important internal daemons used in Spark:
20) What is the method to create a Data frame in Apache Spark?In Apache Spark, we can create a data frame using Tables in Hive and Structured data files. 21) What do you understand by accumulators in Apache Spark?Accumulators are the write-only variables that are initialized once and sent to the workers. Then, these workers update based on the logic written, which will send back to the driver. 22) What is the default level of parallelism in Apache Spark?If it is not specified, then the number of partitions is called the default level of parallelism in Apache Spark. 23) Which companies are using Spark streaming services?The three most famous companies using Spark Streaming services are:
24) Is it possible to use Spark to access and analyze data stored in Cassandra databases?Yes, it is possible to use Spark to access and analyze Cassandra databases' data by using Cassandra Connector. 25) Can we run Apache Spark on Apache Mesos?Yes, we can run Apache Spark on the hardware clusters managed by Mesos. 26) What do you understand by Spark SQL?Spark SQL is a module for structured data processing, which provides the advantage of SQL queries running on that database. 27) How can you connect Spark to Apache Mesos?Follow the steps given below to connect Spark to Apache Mesos:
28) What is the best way to minimize data transfers when working with Spark?To write a fast and reliable Spark program, we have to minimize data transfers and avoid shuffling. There are various ways to minimize data transfers while working with Apache Spark. These are: Using Broadcast Variable- Broadcast variables enhance the efficiency of joins between small and large RDDs. Using Accumulators- Accumulators are used to updating the values of variables in parallel while executing. 29) What do you understand by lazy evaluation in Apache Spark?As the name specifies, lazy evaluation in Apache Spark means that the execution will not start until an action is triggered. In Spark, the lazy evaluation comes into action when Spark transformations occur. Transformations are lazy. When a transformation such as a map() is called on an RDD, it is not performed instantly. Transformations in Spark are not evaluated until you perform an action, which aids in optimizing the overall data processing workflow, known as lazy evaluation. So we can say that in lazy evaluation, data is not loaded until it is necessary. 30) What do you understand by Spark Driver?Spark Driver is the program that runs on the master node of the machine and is used to declare transformations and actions on data RDDs. 31) What is the Parquet file in Apache Spark?Parquet is a column format file supported by many data processing systems. Spark SQL facilitates us to perform both read and write operations with the Parquet file. 32) What is the way to store the data in Apache Spark?Apache Spark is an open-source analytics and processing engine for large-scale data processing, but it does not have any storage engine. It can retrieve data from another storage engine like HDFS, S3. 33) How is it possible to implement machine learning in Apache Spark?Apache Spark itself provides a versatile machine learning library called MLif. By using this library, we can implement machine learning in Spark. 34) What are some disadvantages or demerits of using Apache Spark?Following is the list of some disadvantages or demerits of using Apache Spark:
35) What is the use of File system API in Apache Spark?File system API is used to read data from various storage devices such as HDFS, S3 or Local Files. 36) What are the tasks of a Spark Engine?The main task of a Spark Engine is handling the process of scheduling, distributing and monitoring the data application across the clusters. 37) What is the use of Apache SparkContext?The SparkContent is the entry point to Apache Spark. SparkContext facilitates users to create RDDs, which provide various ways of churning data. 38) Is it possible to do real-time processing with SparkSQL?In SparkSQL, real-time data processing is not possible directly. We can register the existing RDD as a SQL table and trigger the SQL queries on priority. 39) What is the use of Akka in Apache Spark?Akka is used for scheduling in Apache Spark. Spark also uses Akka for messaging between the workers and masters. 40) What do you understand by Spark map() Transformation?Spark map() is a transformation operation used to apply the Transformation on every element of RDD, DataFrame, and Dataset and finally returns a new RDD/Dataset, respectively. 41) What is the advantage of using the Parquet file?In Apache Spark, the Parquet file is used to perform both read and write operations. Following is the list of some advantages of having a Parquet file:
42) What is the difference between persist() and cache() functions in Apache Spark?In Apache Spark, the persist() function is used to allow the user to specify the storage level, whereas the cache() function uses the default storage level. 43) Which Spark libraries allow reliable file sharing at memory speed across different cluster frameworks?Tachyon is the Apache Spark library's name, which is used for reliable file sharing at memory speed across various cluster frameworks. 44) What is shuffling in Apache Spark? When does it occur?In Apache Spark, shuffling is the process of redistributing data across partitions that may lead to data movement across the executors. The implementation of shuffle operation is entirely different in Spark as compared to Hadoop. Shuffling has two important compression parameters:
Shuffling comes in the scene when we join two tables or perform byKey operations such as GroupByKey or ReduceByKey. 45) What are the file formats supported by Apache Spark?Apache Spark supports the file format such as json, tsv, snappy, orc, rc, etc. 46) What are Actions in Apache Spark?In Apache Spark, the action is used to bring back the RDD data to the local machine. Its execution is the result of all previously created transformations. 47) What is Yarn in Apache Spark?Yarn is one of the most important features of Apache Spark. Apache Spark is an in-memory distributed data processing engine, and YARN is a cluster management technology that is used to run Spark. Yarn makes you able to dynamically share and centrally configure the same pool of cluster resources between all frameworks that run on Yarn. When Spark runs on Yarn, it makes the binary distribution as it is built on Yarn support. 48) In which type of machine learning techniques, Apache Spark is the best fit?Apache Spark is the best fit for simple machine learning algorithms like clustering, regression, and classification, etc. 49) What is the use of checkpoints in Apache Spark?In Apache Spark, checkpoints are used to allow the program to run all around the clock. It also helps to make it resilient towards failure irrespective of application logic. 50) What is the lineage in Spark?In Apache Spark, when a transformation (map or filter etc.) is called, it is not executed by Spark immediately; instead, a lineage is created for each transformation. This lineage is used to keep track of what all transformations have to be applied on that RDD. It also traces the location from where it has to read the data. 51) What do you understand by a lineage graph in Spark?In Apache Spark, the lineage graph is a dependencies graph between existing RDD and new RDD. It specifies that all the dependencies between the RDD are recorded in a graph rather than the original data. 52) How can you trigger automatic clean-ups in Spark to handle accumulated metadata?You can trigger the clean-ups by setting the parameter ' Spark.cleaner.ttl' or dividing the long-running jobs into different batches and writing the intermediary results to the disk. 53) Is it possible to launch Spark jobs inside Hadoop MapReduce?Yes, you can run all kinds of spark jobs inside MapReduce without the need to obtain the admin rights of that application. 54) What is the use of BlinkDB in Spark?BlinkDB is a query engine tool used to execute SQL queries on massive volumes of data and renders query results in the meaningful error bars. 55) Can Spark handle monitoring and logging in Standalone mode?Yes. Because of having a web-based user interface, Spark can handle monitoring and logging in standalone mode. 56) How SparkSQL is different from SQL and HQL?SparkSQL is a unique component on the Apache Spark core engine that supports SQL and HQL without changing any syntax. HQL stands for Hive Query Language. You can also join the SQL table and HQL table. |
You may also like:
- Java Interview Questions
- SQL Interview Questions
- Python Interview Questions
- JavaScript Interview Questions
- Angular Interview Questions
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Spring Boot Interview Questions
- HR Interview Questions
- C Programming Interview Questions
- C++ Interview Questions
- Data Structure Interview Questions
- DBMS Interview Questions
- HTML Interview Questions
- IAS Interview Questions
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- OOPs Interview Questions
- .Net Interview Questions
- C# Interview Questions
- ReactJS Interview Questions
- Networking Interview Questions
- PHP Interview Questions
- CSS Interview Questions
- Node.js Interview Questions
- Spring Interview Questions
- Hibernate Interview Questions
- AWS Interview Questions
- Accounting Interview Questions







