What is a Large Language Model (LLM)Technology exists in the quickly developing field of artificial intelligence that has not only pushed the limits of what machines can understand but has also given us a peek into the world of communication that is human-like. The Large Language Model (LLM) is an age-old marvel of technology. The LLM serves as a monument to the amazing advancement made in natural language processing with its capacity to comprehend, produce, and alter human language. In this article, we thoroughly investigate what constitutes a large language model. We will go into its complex design, amazing training process, numerous uses across sectors, difficulties it faces, and moral dilemmas it forces us to face. Describe large language models :LLMs are sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) models that comprehend and produce human language. These deep learning models are distinguished by their enormous size, often made up of billions of parameters. These parameters are the model's teachable components that let it recognize complex patterns, grammatical conventions, and contextual interactions in natural language. 
Large-scale text-based models (LLMs) are trained on massive volumes of text data from various sources, including books, papers, websites, and more. The models can comprehend the syntax, semantics, and even some degree of reasoning inherent in human communication thanks to their broad exposure to various language usages. LLMs often go through two basic rounds of training:Pre-training stage: The model is exposed to the extensive and diverse text dataset during the pre-training stage. It learns to anticipate the following word in a phrase based on the words that came before. In doing so, the model can pick up on linguistic structures and statistical trends in language. Fine-tuning: Pre-training is followed by fine-tuning on certain activities or domains. This entails training the model on a more focused dataset relevant to a specific application, such as translation, summarization, or question answering. The model's outputs can be fine-tuned to work best for a particular job by doing so. LLM's Architectural structureFew developments have captivated the world's interest more than Large Language Models (LLMs) in the complex field of artificial intelligence. These enormous AI creations have the amazing capacity to not only understand the subtleties of human language but also to produce prose that is very human-like. 
The architecture of these models, a thoroughly thought-out blueprint that gives them the ability to absorb, analyze, and manipulate language with astounding competence, is the foundation upon which this linguistic magic is built. In this investigation, we set out on a quest to comprehend the architecture that supports Large Language Models, paying special attention to the transformational Transformer architecture. Important factors influencing the construction of the large language model To modify the behavior, performance, and capabilities of a Large Language Model (LLM), it is necessary to choose and configure various components carefully. The following are the main elements that influence the architecture of an LLM: Model Size and Number of Parameters: Adapting the Complexity of the Model One of the most important factors to consider while creating a Large Language Model (LLM) is the size of the model and the number of parameters it contains.
Models are frequently pre-trained on a wide corpus before being fine-tuned on particular tasks utilizing task-specific data and objectives. Transfer learning uses knowledge acquired during pre-training for jobs farther down the line.
What is prompt engineering?Prompt engineering carefully plans and enhances text prompts for Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 to accomplish certain desired results. Users may actively modify their replies through carefully prepared prompts even though these models already include a wealth of information. An LLM is a chatbot that produces words but doesn't grasp context. The idea is to control the algorithm's input to direct the generated output to match users' objectives successfully. Businesses employ tools and guidance to enhance interactions with their AI apps while this field is still in its infancy. Even compilations of useful prompts are available on some platforms. Prompt engineering is becoming a crucial skill for professionals in both IT and business domains. As organizations seek to leverage LLMs for tailored applications, prompt engineers play a pivotal role in developing customized models that align with specific business needs. As a result, this practice is poised to shape how businesses interact with and utilize LLMs in various industries. Transformer's designAn artificial intelligence model called a transformer-based large language model (LLM) is intended to comprehend, produce, and modify human language. It expands on the Transformer's design, a ground-breaking neural network topology first presented in the 2017 publication "Attention Is All You Need" by Vaswani et al. Since then, complex natural language processing (NLP) models often start with transformers. 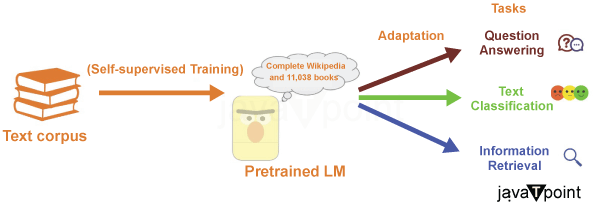
The self-attention mechanism within transformers offers three primary advantages:
In essence, the self-attention mechanism in transformers offers these advantages by efficiently managing computation, enabling parallel processing, and maintaining connections between distant elements in the data. What do the words "autoregressive" and "seq2seq" mean?Answer: Autoregressive describes extrapolating past time steps to anticipate upcoming ones. In the past, this modeling method has been used in industries, including financial forecasting. It is used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) to foresee the next tokens or words in a phrase. Seq2seq is a technique that converts an input sequence into an output sequence. Because the data frequently consists of distinct pieces like letters or tokens in a phrase, the word "sequences" is used. Word embedding techniques turn tokens into numerical vectors to process these elements. The fact that this method can handle a variety of input-output circumstances makes it extremely adaptable and ideal for a wide range of real-world issues. For instance, it can control voice sound bytes, rows of picture pixels, and their related output words. Using sequences to represent data throughout time (such as in speech) and other data layouts has interesting philosophical ramifications. Practically speaking, this adaptability enables categorization tasks like choosing a tweet's emotion from five alternatives and forecasting it. The model can handle a variety of tasks by framing the inquiry and possible responses as sequences of characters (tokens), which is similar to the idea of "artificial general intelligence" (AGI). This implies that a single model may successfully do a variety of jobs. AGI and flexibilityTransformers' rise in popularity is not just a result of their improved performance, which was made possible by using bigger models (a development that frequently showed a linear link with the number of parameters). Even though better precision is unquestionably important in their attractiveness, it only partially explains why transformers have been widely used. Transformers are versatile and relevant across several areas because of their adaptability in handling autoregressive and seq2seq jobs. Therefore, they have an influence beyond simply improving benchmark accuracy. It paves the way for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), a step closer to human-like versatility and adaptability in which a single model can handle various activities. ConclusionIn conclusion, the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) powered by technologies like GPT-3 has drastically changed the landscape of language models. Because of their extraordinary ability to understand context, give thoughtful responses, and even mimic the subtleties of human language, these models have helped usher in a new era of natural language understanding and generation. Throughout this article, we've examined the capabilities, uses, and fundamental workings of LLMs, revealing their capacity for anything from language translation and summarization to creative writing and code production.
Next TopicPrivacy-preserving Machine Learning
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










