Python Tutorial
Python OOPs
Python MySQL
Python MongoDB
Python SQLite
Python Questions
Plotly
Python Tkinter (GUI)
Python Web Blocker
Python MCQ
Related Tutorials
Python Programs
Tqdm Integration with PandasIn this tutorial, we will learn how to implement the tqdm with the pandas library. The tqdm module is used to create the process bar as per the requirement. Process bars are valuable tools for estimating and displaying the time the task will take. To understand this tutorial, you should be familiar with the tqdm module concept and how to create a process bar. We have a complete tutorial on the tqdm module; if you are unfamiliar with the concept, visit the Python tqdm module. Integration with PandasPandas is a famous and useful library used to manipulate numerical data. It is one of the most commonly used libraries for handling tabular data. Pandas represent the data in two different ways - Series and Dataframe. Dataframe is a tabular structure with rows and columns and can also represent heterogeneous data. This library is built upon the Numpy library; it is extensively used in the field of Data Science. To use the pandas library, we need to install it in our system using the pip command. Example - Output:
0 1 2 3 4
0 86 39 1 45 59
1 77 29 52 86 68
2 25 33 39 75 57
3 45 72 83 0 50
4 5 8 8 33 15
5 39 35 9 57 5
6 47 90 97 94 25
7 74 59 51 42 27
8 58 75 42 80 41
9 92 73 4 45 80
pandas tqdm integration demo: 100%|????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????| 100/100 [00:00<00:00, 659.65it/s]
0 1 2 3 4
0 91 44 6 50 64
2 30 38 44 80 62
3 50 77 88 5 55
4 10 13 13 38 20
5 44 40 14 62 10
6 52 95 102 99 30
7 79 64 56 47 32
8 63 80 47 85 46
9 97 78 9 50 85
In the above code, we have imported the pandas and tqdm library and initialized the dataframe size 100 x 100 with random integers between 0 and 100. Then we used the tqdm.pandas method to specify the pandas.progress_apply function with tqdm. We use the process_apply function in place of apply function. This function is used to display the tqdm bar to denote the percentage of progress. Both apply, and the process_apply() function takes a function as a parameter. In our code, we have passed the lambda function that takes a number, adds 10 and returns it. Tqdm NotebookJupiter notebook is open-source and supports multiple programming languages such as Python and R. However; it is popular among Python developers. It provides a live and interactive Python runtime environment. Jupyter notebook is quite popular among ML practitioners and data engineers, and it helps to inspect the data or test step-by-step. We can display tqdm loaders inside a Jupyter notebook. To do so, we first need to setup the Jupyter notebook in the system. After setting up this, we need to install tqdm.notebook module, which is similar to the tqdm. Open a notebook and run pip install ipywidgets to ensure that the progress bar is displayed dynamically updated in the notebook. The tqdm bar comes in three colors. Green indicates the successfully completed progress, blue is for an ongoing process, and red indicates that it has been terminated midway. Example - Output - Output for an ongoing process - 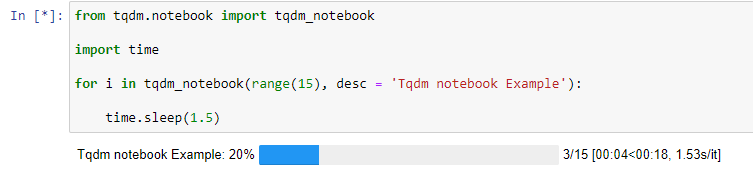
Output for successful process - 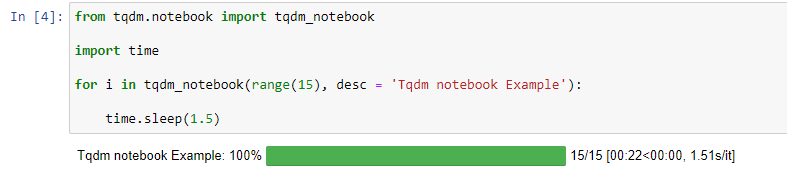
The tqdm_notebook should be wrapped around an iterable same as the tqdm. The Jupyter notebook can implement all the functions and features of the tqdm library. For example - The desc keyword is used to print the description of the progress bar, the total iteration, etc. Alternative to tqdmThe tqdm is a handy and powerful tool to track the progress of the process in Python. Apart from that, many other libraries can also be used to achieve the same or similar goal. A few of these libraries are processbar, processbar2, and alive-process. The processbar library is pretty simple and printed with the # symbol. We can also print the process bar as a spinner like the loading circle shown in the web browser. But it creates a problem with the print statement and the process bar. After every print statement, a new progress bar is displayed. To overcome this, we can use the progressbar2 library, which allows standard redirect to output, able to use the print statement along with the clean progress bar. The last alternative library is alive-process which offers some attractive progress bars. You can use the alive-progress library if you need an animated progress bar. Advantages of tqdmFollowing are the benefits of the tqdm library.
ConclusionThis tutorial included the implementation of tqdm with the pandas library. We have explored its features and advantages. Instead of using the tqdm library, we can use its alternative libraries such as processbar, processbar2 and alive-progress. It offers multiple benefits like a visual estimation of the progress of your task, and it indicates when an issue or error encounters in the program. It also estimates the time required to complete the task. We can also apply multiple customizations as the project requirement, which is low overhead and a smart progress bar.
Next TopicBisect Module in Python
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










